Copper transport into the secretory pathway is regulated by oxygen in macrophages
- PMID: 19351718
- PMCID: PMC2671928
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.043216
Copper transport into the secretory pathway is regulated by oxygen in macrophages
Abstract
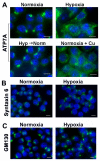
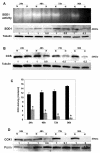
Copper is an essential nutrient for a variety of biochemical processes; however, the redox properties of copper also make it potentially toxic in the free form. Consequently, the uptake and intracellular distribution of this metal is strictly regulated. This raises the issue of whether specific pathophysiological conditions can promote adaptive changes in intracellular copper distribution. In this study, we demonstrate that oxygen limitation promotes a series of striking alterations in copper homeostasis in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Hypoxia was found to stimulate copper uptake and to increase the expression of the copper importer, CTR1. This resulted in increased copper delivery to the ATP7A copper transporter and copper-dependent trafficking of ATP7A to cytoplasmic vesicles. Significantly, the ATP7A protein was required to deliver copper into the secretory pathway to ceruloplasmin, a secreted copperdependent enzyme, the expression and activity of which were stimulated by hypoxia. However, the activities of the alternative targets of intracellular copper delivery, superoxide dismutase and cytochrome c oxidase, were markedly reduced in response to hypoxia. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that copper delivery into the biosynthetic secretory pathway is regulated by oxygen availability in macrophages by a selective increase in copper transport involving ATP7A.
Figures




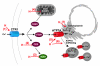
References
-
- Alessandri, G., Raju, K. and Gullino, P. M. (1984). Angiogenesis in vivo and selective mobilization of capillary endothelium in vitro by heparin-copper complex. Microcirc. Endothelium Lymphatics 1, 329-346. - PubMed
-
- Amaravadi, R., Glerum, D. M. and Tzagoloff, A. (1997). Isolation of a cDNA encoding the human homolog of COX17, a yeast gene essential for mitochondrial copper recruitment. Hum. Genet. 99, 329-333. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, N., Tsivkovskii, R., Tsivkovskaia, N. and Lutsenko, S. (2005). The copper-transporting ATPases, menkes and wilson disease proteins, have distinct roles in adult and developing cerebellum. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 9640-9645. - PubMed
-
- Biswas, S. K., Gangi, L., Paul, S., Schioppa, T., Saccani, A., Sironi, M., Bottazzi, B., Doni, A., Vincenzo, B., Pasqualini, F. et al. (2006). A distinct and unique transcriptional program expressed by tumor-associated macrophages (defective NF-kappaB and enhanced IRF-3/STAT1 activation). Blood 107, 2112-2122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

