Noninvasive detection of EGFR T790M in gefitinib or erlotinib resistant non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 19351754
- PMCID: PMC2727796
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2592
Noninvasive detection of EGFR T790M in gefitinib or erlotinib resistant non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Tumors from 50% of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients that develop resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib will contain a secondary EGFR T790M mutation. As most patients do not undergo repeated tumor biopsies we evaluated whether EGFR T790M could be detected using plasma DNA.
Experimental design: DNA from plasma of 54 patients with known clinical response to gefitinib or erlotinib was extracted and used to detect both EGFR-activating and EGFR T790M mutations. Forty-three (80%) of patients had tumor EGFR sequencing (EGFR mutant/wild type: 30/13) and seven patients also had EGFR T790M gefitinib/erlotinib-resistant tumors. EGFR mutations were detected using two methods, the Scorpion Amplification Refractory Mutation System and the WAVE/Surveyor, combined with whole genome amplification.
Results: Both EGFR-activating and EGFR T790M were identified in 70% of patients with known tumor EGFR-activating (21 of 30) or T790M (5 of 7) mutations. EGFR T790M was identified from plasma DNA in 54% (15 of 28) of patients with prior clinical response to gefitinib/erlotinib, 29% (4 of 14) with prior stable disease, and in 0% (0 of 12) that had primary progressive disease or were untreated with gefitinib/erlotinib.
Conclusions: EGFR T790M can be detected using plasma DNA from gefitinib- or erlotinib-resistant patients. This noninvasive method may aid in monitoring drug resistance and in directing the course of subsequent therapy.
Figures
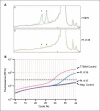
References
-
- Inoue A, Suzuki T, Fukuhara T, et al. Prospective phase II study of gefitinib for chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3340–6. - PubMed
-
- Paz-Ares L, Sanchez JM, GarcIía-Velasco A, et al. A prospective phase II trial of erlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (p) with mutations in the tyrosine kinase (TK) domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) J Clin Oncol. 2006;24 Abstract 7020.
-
- Sequist LV, Martins RG, Spigel D, et al. First-line gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring somatic EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2442–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

