Fine mapping of chromosome 6q23-25 region in familial lung cancer families reveals RGS17 as a likely candidate gene
- PMID: 19351763
- PMCID: PMC2746091
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2335
Fine mapping of chromosome 6q23-25 region in familial lung cancer families reveals RGS17 as a likely candidate gene
Abstract
Purpose: We have previously mapped a major susceptibility locus influencing familial lung cancer risk to chromosome 6q23-25. However, the causal gene at this locus remains undetermined. In this study, we further refined this locus to identify a single candidate gene, by fine mapping using microsatellite markers and association studies using high-density single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP).
Experimental design: Six multigenerational families with five or more affected members were chosen for fine-mapping the 6q linkage region using microsatellite markers. For association mapping, we genotyped 24 6q-linked cases and 72 unrelated noncancer controls from the Genetic Epidemiology of Lung Cancer Consortium resources using the Affymetrix 500K chipset. Significant associations were validated in two independent familial lung cancer populations: 226 familial lung cases and 313 controls from the Genetic Epidemiology of Lung Cancer Consortium, and 154 familial cases and 325 controls from Mayo Clinic. Each familial case was chosen from one high-risk lung cancer family that has three or more affected members.
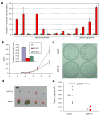
Results: A region-wide scan across 6q23-25 found significant association between lung cancer susceptibility and three single nucleotide polymorphisms in the first intron of the RGS17 gene. This association was further confirmed in two independent familial lung cancer populations. By quantitative real-time PCR analysis of matched tumor and normal human tissues, we found that RGS17 transcript accumulation is highly and consistently increased in sporadic lung cancers. Human lung tumor cell proliferation and tumorigenesis in nude mice are inhibited upon knockdown of RGS17 levels.
Conclusion: RGS17 is a major candidate for the familial lung cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 6q23-25.
Figures


Comment in
-
Lung cancer genetics: a family affair?Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Apr 15;15(8):2581-2. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0003. Epub 2009 Apr 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19351746
References
-
- Heath CW. Differences between smokers and nonsmokers. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1958;101:377–88. - PubMed
-
- Motulsky AG. Drug reactions enzymes, and biochemical genetics. J Am Med Assoc. 1957;165:835–7. - PubMed
-
- Tokuhata GK, Lilienfeld AM. Familial aggregation of lung cancer in humans. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1963;30:289–312. - PubMed
-
- Fraumeni JF, Wertelecki W, Blattner WA, Jensen RD, Leventhal BG. Varied manifestations of a familial lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Med. 1975;59:145–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA063700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES012063/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES013340/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA63700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA093643/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA 15083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA070907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA099187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES013340/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065404/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DE-FGB-95ER62060/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA058554/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA70907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA076293/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA099187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058554/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA22453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES006096/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA099147/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA80127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30ES06096/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA099147/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA093643/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA022453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES012063/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA76293/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC35145/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA077118/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

