PTEN loss contributes to erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer by activation of Akt and EGFR
- PMID: 19351834
- PMCID: PMC2849653
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4055
PTEN loss contributes to erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer by activation of Akt and EGFR
Erratum in
-
Correction: PTEN Loss Contributes to Erlotinib Resistance in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer by Activation of Akt and EGFR.Cancer Res. 2015 May 1;75(9):1922. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0822. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25934712 No abstract available.
-
Editor's Note: PTEN Loss Contributes to Erlotinib Resistance in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer by Activation of Akt and EGFR.Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 3;85(5):1003. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-5044. Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40025966 No abstract available.
Abstract
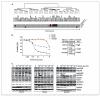
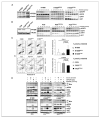
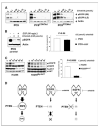
Clinical resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibition in lung cancer has been linked to the emergence of the EGFR T790M resistance mutation or amplification of MET. Additional mechanisms contributing to EGFR inhibitor resistance remain elusive. By applying combined analyses of gene expression, copy number, and biochemical analyses of EGFR inhibitor responsiveness, we identified homozygous loss of PTEN to segregate EGFR-dependent and EGFR-independent cells. We show that in EGFR-dependent cells, PTEN loss partially uncouples mutant EGFR from downstream signaling and activates EGFR, thereby contributing to erlotinib resistance. The clinical relevance of our findings is supported by the observation of PTEN loss in 1 out of 24 primary EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumors. These results suggest a novel resistance mechanism in EGFR-mutant NSCLC involving PTEN loss.
Figures

References
-
- Sharma SV, Fischbach MA, Haber DA, Settleman J. “Oncogenic shock”: explaining oncogene addiction through differential signal attenuation. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:4392–5s. - PubMed
-
- Thomas RK, Greulich H, Yuza Y, et al. Detection of oncogenic mutations in the EGFR gene in lung adenocarcinoma with differential sensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Janne PA. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2895–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

