Toll-like receptors in kidney disease
- PMID: 19352178
- PMCID: PMC2896868
- DOI: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32832a1d5f
Toll-like receptors in kidney disease
Abstract
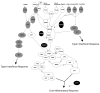
Purpose of review: The innate immune system is our first line of defense against infection and injury, and responsible for initiating inflammatory and immune responses to resolve infections and repair injured tissues. This review focuses on the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) of the innate immune system and their role in recognizing infection and injury, and regulating inflammatory responses in the kidney.
Recent findings: There is increasing data to support a role for TLRs in immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis. TLR7 has emerged as a key regulator of autoantibody production in murine lupus nephritis. In addition, studies have implicated TLR recognition of endogenous molecules released during cellular necrosis as critical regulators of sterile inflammation and injury. Tonic interactions between TLRs and environmental agonists derived from commensal microbes and endogenous sources may also influence autoimmune disease and inflammatory disorders affecting the kidney.
Conclusion: Future studies to decipher the contribution of TLRs and other innate immune receptors in the regulation of inflammation, immune responses, and injury in the kidney will pave the way for novel therapeutic interventions.
Figures

References
-
- Jin MS, Kim SE, Heo JY. Crystal structure of the TLR1-TLR2 heterodimer induced by binding of a tri-acylated lipopeptide. Cell. 2007;130:1071–1082. - PubMed
-
- Kim HM, Park BS, Kim JI. Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist eritoran. Cell. 2007;130:906–917. - PubMed
-
- Cirl C, Wieser A, Yadav M. Subversion of Toll-like receptor signaling by a unique family of bacterial Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing proteins. Nat Med. 2008;14:399–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

