Ubiquitin-like protein activation by E1 enzymes: the apex for downstream signalling pathways
- PMID: 19352404
- PMCID: PMC2712597
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm2673
Ubiquitin-like protein activation by E1 enzymes: the apex for downstream signalling pathways
Abstract
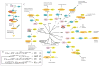
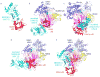
Attachment of ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like proteins (known as UBLs) to their targets through multienzyme cascades is a central mechanism to modulate protein functions. This process is initiated by a family of mechanistically and structurally related E1 (or activating) enzymes. These activate UBLs through carboxy-terminal adenylation and thiol transfer, and coordinate the use of UBLs in specific downstream pathways by charging cognate E2 (or conjugating) enzymes, which then interact with the downstream ubiquitylation machinery to coordinate the modification of the target. A broad understanding of how E1 enzymes activate UBLs and how they selectively coordinate UBLs with downstream function has come from enzymatic, structural and genetic studies.
Figures
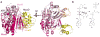

References
-
- Ciechanover A. Intracellular protein degradation: from a vague idea, through the lysosome and the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and onto human diseases and drug targeting (Nobel lecture) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2005;44:5944–5967. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg AL. Functions of the proteasome: from protein degradation and immune surveillance to cancer therapy. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Heller H, Elias S, Ciechanover A. Components of ubiquitin-protein ligase system. Resolution, affinity purification, and role in protein breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:8206–8214. Describes the chromatographic separation of E1, E2 and E3 activities and demonstrates reconstitution of the first ubiquitin ligase reaction. - PubMed
-
- Hochstrasser M. Lingering mysteries of ubiquitin-chain assembly. Cell. 2006;124:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Pickart CM, Fushman D. Polyubiquitin chains: polymeric protein signals. CurrOpin Chem Biol. 2004;8:610–616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

