Recurrence of atrial fibrillation correlates with the extent of post-procedural late gadolinium enhancement: a pilot study
- PMID: 19356576
- PMCID: PMC2703450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2008.10.016
Recurrence of atrial fibrillation correlates with the extent of post-procedural late gadolinium enhancement: a pilot study
Abstract
Objectives: We sought to evaluate radiofrequency (RF) ablation lesions in atrial fibrillation (AF) patients using cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR), and to correlate the ablation patterns with treatment success.
Background: RF ablation procedures for treatment of AF result in localized scar that is detected by late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) CMR. We hypothesized that the extent of scar in the left atrium and pulmonary veins (PV) would correlate with moderate-term procedural success.
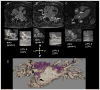
Methods: Thirty-five patients with AF, undergoing their first RF ablation procedure, were studied. The RF ablation procedure was performed to achieve bidirectional conduction block around each PV ostium. AF recurrence was documented using a 7-day event monitor at multiple intervals during the first year. High spatial resolution 3-dimensional LGE CMR was performed 46 +/- 28 days after RF ablation. The extent of scarring around the ostia of each PV was quantitatively (volume of scar) and qualitatively (1: minimal, 3: extensive and circumferential) assessed.
Results: Thirteen (37%) patients had recurrent AF during the 6.7 +/- 3.6-month observation period. Paroxysmal AF was a strong predictor of nonrecurrent AF (15% with recurrence vs. 68% without, p = 0.002). Qualitatively, patients without recurrence had more completely circumferentially scarred veins (55% vs. 35% of veins, p = NS). Patients without recurrence more frequently had scar in the inferior portion of the right inferior pulmonary vein (RIPV) (82% vs. 31%, p = 0.025, Bonferroni corrected). The volume of scar in the RIPV was quantitatively greater in patients without AF recurrence (p < or = 0.05) and was a univariate predictor of recurrence using Cox regression (p = 0.049, Bonferroni corrected).
Conclusions: Among patients undergoing PV isolation, AF recurrence during the first year is associated with a lesser degree of PV and left atrial scarring on 3-dimensional LGE CMR. This finding was significant for RIPV scar and may have implications for the procedural technique used in PV isolation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance in the world of the cardiac electrophysiologist: the road to real-time cardiac magnetic resonance.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009 Mar;2(3):317-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2008.12.009. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19356577 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pappone C, Rosanio S, Oreto G, Tocchi M, Gugliotta F, Vicedomini G, Salvati A, Dicandia C, Mazzone P, Santinelli V, Gulletta S, Chierchia S. Circumferential radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary vein ostia: A new anatomic approach for curing atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2000;102:2619–2628. - PubMed
-
- Essebag V, Wylie JV, Josephson ME. Effectiveness of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:130–131. - PubMed
-
- Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J, Kim YH, Klein G, Packer D, Skanes A. Worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2005;111:1100–1105. - PubMed
-
- Oral H, Knight BP, Tada H, Ozaydin M, Chugh A, Hassan S, Scharf C, Lai SW, Greenstein R, Pelosi F, Jr, Strickberger SA, Morady F. Pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2002;105:1077–1081. - PubMed
-
- Verma A, Kilicaslan F, Pisano E, Marrouche NF, Fanelli R, Brachmann J, Geunther J, Potenza D, Martin DO, Cummings J, Burkhardt JD, Saliba W, Schweikert RA, Natale A. Response of atrial fibrillation to pulmonary vein antrum isolation is directly related to resumption and delay of pulmonary vein conduction. Circulation. 2005;112:627–635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

