Validation of five-colony pool analysis using multiplex real-time PCR for detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 19357211
- PMCID: PMC2691103
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00608-09
Validation of five-colony pool analysis using multiplex real-time PCR for detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
Five Escherichia coli colonies/patient were studied to evaluate the reliability of a multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli groups, using a pool of five colonies rather than individual colonies. Sensitivity and specificity were 98% and 100%, respectively, at a fifth of the cost of the individual colony analysis.
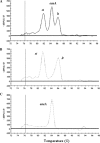
Figures
References
-
- Black, R. E., S. S. Morris, and J. Bryce. 2003. Where and why are 10 million children dying every year? Lancet 3612226-2234. - PubMed
-
- Bryce, J., C. Boschi-Pinto, K. Shibuya, R. E. Black, and the WHO Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group. 2005. WHO estimates of the causes of death in children. Lancet 3651147-1152. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, M. B., J. P. Nataro, D. I. Bernstein, J. Hawkins, N. Roberts, and M. A. Staat. 2005. Prevalence of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in acute childhood enteritis: a prospective controlled study. J. Pediatr. 14654-61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

