Activity profiles of cholinergic and intermingled GABAergic and putative glutamatergic neurons in the pontomesencephalic tegmentum of urethane-anesthetized rats
- PMID: 19357291
- PMCID: PMC6665745
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5502-08.2009
Activity profiles of cholinergic and intermingled GABAergic and putative glutamatergic neurons in the pontomesencephalic tegmentum of urethane-anesthetized rats
Abstract
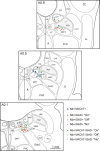
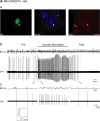
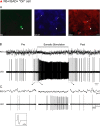
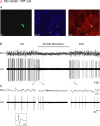
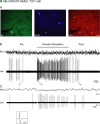
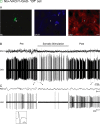
Cholinergic neurons in the pontomesencephalic tegmentum form part of the ascending activating system and are thought to participate in stimulating cortical activation. Yet in the laterodorsal tegmental and pedunculopontine tegmental nuclei (LDT and PPT), they lie intermingled with GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons, which could also modulate cortical activity and sleep-wake state. To characterize the discharge of these cell types in relation to cortical activity, we recorded neurons in urethane-anesthetized rats during spontaneous slow wave and somatosensory evoked fast electroencephalographic (EEG) activity, then labeled the cells by juxtacellular technique with Neurobiotin (Nb) and dual-immunostained them for vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) and glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). All cholinergic cells discharged minimally during prestimulation (approximately 0.5 Hz) and moderately in a tonic manner (approximately 4 Hz) during stimulation. Being heterogeneous, some GABAergic, called "On," cells (approximately 48%) increased their discharge (from approximately 4 to 7 Hz), whereas others, called "Off" cells (approximately 38%), decreased or ceased firing during stimulation. Similarly, some noncholinergic/non-GABAergic On cells increased (from approximately 2 to 6 Hz, approximately 49%), whereas other Off cells decreased firing ( approximately 35%) during stimulation. Putative glutamatergic On together with GABAergic On neurons could thus act in parallel with cholinergic cells to stimulate cortical activation. Possibly influenced by cholinergic On and glutamatergic Off cells, whose change in discharge precedes theirs, the GABAergic Off cells could oppose neighboring neurons such as noradrenergic cells, which discharge during waking and cease firing during sleep. By concerted activity, these heterogeneous cell groups can modulate cortical activity and behavioral state across the sleep-waking cycle.
Figures
References
-
- Amatruda TT, 3rd, Black DA, McKenna TM, McCarley RW, Hobson JA. Sleep cycle control and cholinergic mechanisms: differential effects of carbachol injections at pontine brain stem sites. Brain Res. 1975;98:501–515. - PubMed
-
- Brischoux F, Mainville L, Jones BE. Muscarinic-2 and orexin-2 receptors on GABAergic and other neurons in the rat mesopontine tegmentum and their potential role in sleep-wake state control. J Comp Neurol. 2008;510:607–630. - PubMed
-
- Brown RE, McKenna JT, Winston S, Basheer R, Yanagawa Y, Thakkar MM, McCarley RW. Characterization of GABAergic neurons in rapid-eye-movement sleep controlling regions of the brainstem reticular formation in GAD67-green fluorescent protein knock-in mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:352–363. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
