Initiating delivery room stabilization/resuscitation in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants with an FiO(2) less than 100% is feasible
- PMID: 19357695
- PMCID: PMC2834356
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2009.34
Initiating delivery room stabilization/resuscitation in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants with an FiO(2) less than 100% is feasible
Abstract
Background: Oxygen exposure during delivery room (DR) resuscitation, even when brief, is potentially toxic. A practice plan (PP) was introduced for very low birth weight (VLBW) infants < or = 1500 g as follows: initial FiO(2) from 0.21 to 1.0 using blenders, oxygen guided by oximetry to maintain saturation between 85% to 95% from birth.
Objective: To determine whether the initiating FiO(2) could be safely lowered, and by doing so whether the number of infants with a PaO(2) >80 mm Hg could be minimized on admission, as well as lowering oxygen requirement at 24 h.
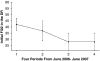
Methods: In all, 53 infants admitted between June 2006 and June 2007 were evaluated and compared with 47 infants from 2004 managed with 100 % oxygen (historical comparison group (HC)).
Result: Stabilization/Resuscitation included intubation (n=28) and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) (n=25); no cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). The heart rate increased rapidly in all cases. The initiating FiO(2) decreased from 0.42 to 0.28 over 12 months (P=0.00005); 14 (26%) were resuscitated with room air. Correspondingly, the pH increased from 7.24 to 7.30 (P=0.002) and PCO(2) decreased from 53 to 41 (P=0.001). A comparison of infants during the PP with the HC revealed that 36/53 versus 21/47 had an initial PaO(2) <80 mm Hg (P=0.02); the median PaO(2), that is, 64 versus 86 and saturation, that is, 95% versus 99% on admission were significantly lower. The median FiO(2) at 24 h was 0.25 versus 0.40.
Conclusion: DR resuscitation of VLBW infants can be initiated with less oxygen even with room air without concomitant overt morbidity. This change was associated with more infants with an initial PaO(2) <80 mm Hg and lower saturation values on admission as well as a lower FiO(2) requirement at 24 h.
Figures
Comment in
-
Initiating preterm resuscitation with less than 100% oxygen.J Perinatol. 2010 May;30(5):366; author reply 367-8. doi: 10.1038/jp.2010.2. J Perinatol. 2010. PMID: 20428181 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rootwelt T, Løberg EM, Moen A, Oyasaeter S, Saugstad OD. Hypoxemia and reoxygenation with 21 or 100% oxygen in newborn pigs: changes in blood pressure, base deficit, and hypoxanthine and brain morphology. Pediatr Res. 1992;32:107–113. - PubMed
-
- Rootwelt T, Odden JP, Hall C, Ganes T, Saugstad OD. Cerebral blood flow and evoked potentials during reoxygenation with 21 or 100% O2 in newborn pigs. J Appl Physiol. 1993;75:2054–2060. - PubMed
-
- Rootwelt T, Odden JP, Hall C, Saugstad OD. Regional blood flow during severe hypoxemia and resuscitation with 21 or 100% in newborn pigs. J Perinat Med. 1996;24:227–236. - PubMed
-
- Poulsen JP, Øyasæter S, Saugstad OD. Hypoxanthine, xanthine, and uric acid in newborn pigs during hypoxemia followed by resuscitation with room air or 100% oxygen. Crit Care Med. 1993;21:1058–1065. - PubMed
-
- Tølløfsrud PA, Solås AB, Saugstad OD. Newborn piglets with meconium aspiration resuscitated with room air or 100% oxygen. Pediatr Res. 2001;50:423–429. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous