Lifelong impact of variations in maternal care on dendritic structure and function of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in rat offspring
- PMID: 19357777
- PMCID: PMC2663818
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005167
Lifelong impact of variations in maternal care on dendritic structure and function of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in rat offspring
Abstract
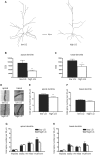
Maternal licking and grooming (LG) exerts profound influence on hippocampal development and function in the offspring. However, little information is available on the effects of variations in maternal care on other brain regions. Here we examined the effects of variation in the frequency of maternal LG on morphological and electrophysiological properties of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in the somatosensory cortex in adult offspring. Compared to low LG offspring, high LG offspring displayed decreased dendritic complexity, reduced spine density and decreased amplitude of spontaneous postsynaptic currents. These changes were accompanied by higher levels of reelin expression in offspring of high LG mothers. Taken together, these findings suggest that differential amount of naturally-occurring variations in maternal LG is associated with enduring changes in dendritic morphology and synaptic function in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons of the somatosensory cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Maternal care influences hippocampal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function and dynamic regulation by corticosterone in adulthood.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Sep 15;72(6):491-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.03.016. Epub 2012 Apr 21. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22521150
-
Variations of maternal care alter offspring levels of behavioural defensiveness in adulthood: evidence for a threshold model.Behav Brain Res. 2007 Jan 25;176(2):302-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.10.014. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Behav Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17084914
-
Implications of temporal variation in maternal care for the prediction of neurobiological and behavioral outcomes in offspring.Behav Neurosci. 2013 Feb;127(1):33-46. doi: 10.1037/a0031219. Behav Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23398440 Free PMC article.
-
Reelin, neuronal polarity and process orientation of cortical neurons.Neuroscience. 2014 Jun 6;269:102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.03.004. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24657457 Review.
-
Role of Reelin in the development and maintenance of cortical lamination.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009 Nov;116(11):1451-5. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0228-7. Epub 2009 Apr 25. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009. PMID: 19396394 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune deficiency influences juvenile social behavior and maternal behavior.Behav Neurosci. 2015 Jun;129(3):331-8. doi: 10.1037/bne0000053. Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26030431 Free PMC article.
-
Development of individual differences in stress responsiveness: an overview of factors mediating the outcome of early life experiences.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Mar;214(1):141-54. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2118-y. Epub 2010 Dec 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21165737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individual differences in cortical connections of somatosensory cortex are associated with parental rearing style in prairie voles (Microtus ochrogaster).J Comp Neurol. 2016 Feb 15;524(3):564-77. doi: 10.1002/cne.23837. Epub 2015 Jul 18. J Comp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26101098 Free PMC article.
-
Reelin Regulates the Maturation of Dendritic Spines, Synaptogenesis and Glial Ensheathment of Newborn Granule Cells.Cereb Cortex. 2016 Oct 17;26(11):4282-4298. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhw216. Cereb Cortex. 2016. PMID: 27624722 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of maternal care on the developing brain: Mechanisms, temporal dynamics and sensitive periods.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016 Jan;40:52-66. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26616341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oakley Browne MA, Joyce PR, Wells JE, Bushnell JA, Hornblow AR. Disruptions in childhood parental care as risk factors for major depression in adult women. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 1995;29:437–448. - PubMed
-
- Liu D, Dioro J, Tannenbaum B, Caldji, Francis D, et al. Maternal care, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. Science. 1997;277:1659–1662. - PubMed
-
- Bredy TW, Grant RJ, Champagne DL, Meaney MJ. Maternal care influences neuronal survival in the hippocampus of the rat. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18:2903–2909. - PubMed
-
- Liu D, Dioro J, Day JC, Francis DD, Meaney MJ. Maternal care, hippocampal synaptogenesis and cognitive development in rats. Nat Neurosci. 2000;8:799–806. - PubMed
-
- Cameron NM, Shahrokh D, Del Corpo A, Dhir SK, Szyf M, et al. Epigenetic programming of phenotypic variations in reproductive strategies in the rat through maternal care. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008;20:795–801. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

