Determinants of friction in soft elastohydrodynamic lubrication
- PMID: 19358993
- PMCID: PMC2683914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.02.021
Determinants of friction in soft elastohydrodynamic lubrication
Abstract
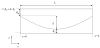
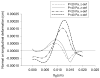
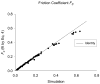
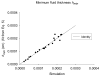
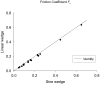
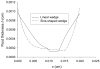
Elastohydrodynamic lubrication (EHL) protects soft tissues from damage and wear in many biological systems (e.g. synovial joints, cornea of the eye, and pleural surfaces of the lung and chest wall). Among studies of lubrication of deformable solids, few have examined the effects of external loads, geometry, and material properties on EHL of soft tissues. To examine these effects, we studied the tribology of soft tissues in a two-dimensional finite element simulation of a thin layer of fluid separating a sliding rigid surface from a soft asperity or bump with an initial sinusoidal shape. We computed the frictional force, deformation of the solid, and change in fluid thickness as functions of independent variables: sliding velocity, normal load, material properties, and bump amplitude and length. Double-logarithmic regression was used to determine the exponents of the scaling relationships of friction coefficient and minimum fluid thickness to the independent variables. The analysis showed that frictional shear force is strongly dependent on velocity, viscosity, and load, moderately dependent on bump length and elasticity, and only weakly dependent on the bump amplitude. The minimum fluid thickness is strongly dependent on velocity and viscosity, and changes moderately with load, elasticity, amplitude, and length. The shape of the bump has little effect. The results confirm that the shear-induced deformation of an initially symmetrical shape, including generalizations to other symmetrical geometries such as quadratic or piecewise linear bumps, leads to load-supporting behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or other interest that could affect the objectivity with which they approach the subject matter of this investigation.
Figures




References
-
- Dowson D, Jin ZM. Micro-elastohydrodynamic lubrication of synovial joints. Engineering in Medicine. 1986;15:63–5. - PubMed
-
- Dowson D, Jin ZM. Microelastohydrodynamic lubrication of low-elastic-modulus solids on rigid substrates. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics. 1992;25:A116–A123.
-
- Gouldstone A, Brown RE, Butler JP, Loring SH. Elastohydrodynamic separation of pleural surfaces during breathing. Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology. 2003;137:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Hamrock BJ. Fundamentals of fluid film lubrication. McGraw-Hill; 1994. p. 42.
-
- Jin ZM, Dowson D. A general analytical solution to the problem of microelastohydrodynamic lubrication of low elastic modulus compliant bearing surfaces under line contact conditions. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers; 1997. pp. 265–272.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

