Determination of gene expression patterns using high-throughput RNA in situ hybridization to whole-mount Drosophila embryos
- PMID: 19360017
- PMCID: PMC2780369
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2009.55
Determination of gene expression patterns using high-throughput RNA in situ hybridization to whole-mount Drosophila embryos
Abstract
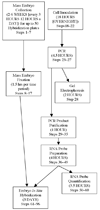
We describe a high-throughput protocol for RNA in situ hybridization (ISH) to Drosophila embryos in a 96-well format. cDNA or genomic DNA templates are amplified by PCR and then digoxigenin-labeled ribonucleotides are incorporated into antisense RNA probes by in vitro transcription. The quality of each probe is evaluated before ISH using a RNA probe quantification (dot blot) assay. RNA probes are hybridized to fixed, mixed-staged Drosophila embryos in 96-well plates. The resulting stained embryos can be examined and photographed immediately or stored at 4 degrees C for later analysis. Starting with fixed, staged embryos, the protocol takes 6 d from probe template production through hybridization. Preparation of fixed embryos requires a minimum of 2 weeks to collect embryos representing all stages. The method has been used to determine the expression patterns of over 6,000 genes throughout embryogenesis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High-resolution in situ hybridization to whole-mount zebrafish embryos.Nat Protoc. 2008;3(1):59-69. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.514. Nat Protoc. 2008. PMID: 18193022
-
Multi-target Chromogenic Whole-mount In Situ Hybridization for Comparing Gene Expression Domains in Drosophila Embryos.J Vis Exp. 2016 Jan 31;(107):e53830. doi: 10.3791/53830. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 26862978 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of gene expression patterns using in situ hybridization to Drosophila testes.Nat Protoc. 2009;4(12):1807-19. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.192. Nat Protoc. 2009. PMID: 20010932
-
Impressive expressions: developing a systematic database of gene-expression patterns in Drosophila embryogenesis.Genome Biol. 2003;4(2):205. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-2-205. Epub 2003 Jan 28. Genome Biol. 2003. PMID: 12620112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole mount in situ hybridization techniques for analysis of the spatial distribution of mRNAs in sea urchin embryos and early larvae.Methods Cell Biol. 2019;151:177-196. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2019.01.003. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Methods Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30948007 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods and tools for spatial mapping of single-cell RNAseq clusters in Drosophila.Genetics. 2021 Apr 15;217(4):iyab019. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab019. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33713129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Z Probe, An Efficient Tool for Characterizing Long Non-Coding RNA in FFPE Tissues.Noncoding RNA. 2018 Sep 5;4(3):20. doi: 10.3390/ncrna4030020. Noncoding RNA. 2018. PMID: 30189670 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into Notch Signaling Steps That Involve pecanex from Dominant-Modifier Screens in Drosophila.Genetics. 2018 Aug;209(4):1099-1119. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.300935. Epub 2018 May 31. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29853475 Free PMC article.
-
A six-amino-acid motif is a major determinant in functional evolution of HOX1 proteins.Genes Dev. 2020 Dec 1;34(23-24):1680-1696. doi: 10.1101/gad.342329.120. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 33184220 Free PMC article.
-
Syndecan receptors: pericellular regulators in development and inflammatory disease.Open Biol. 2021 Feb;11(2):200377. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200377. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Open Biol. 2021. PMID: 33561383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jones KW, Robertson FW. Localisation of reiterated nucleotide sequences in Drosophila and mouse by in situ hybridisation of complementary RNA. Chromosoma. 1970;31:331–345. - PubMed
-
- Harrison PR, Conkie D, Paul J, Jones K. Localisation of cellular globin messenger RNA by in situ hybridisation to complementary DNA. FEBS Lett. 1973;32:109–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

