A compendium of potential biomarkers of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 19360088
- PMCID: PMC2661257
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000046
A compendium of potential biomarkers of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Akhilesh Pandey and colleagues describe a compendium of potential biomarkers that can be systematically validated by the pancreatic cancer community.
Conflict of interest statement
RHH has the potential to receive milestone payments and royalties from Anza Therapeutics as a result of the mesothelin invention.
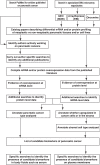
Figures

References
-
- Hawes RH, Xiong Q, Waxman I, Chang KJ, Evans DB, et al. A multispecialty approach to the diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Mathivanan S, Ahmed M, Ahn NG, Alexandre H, Amanchy R, et al. Human Proteinpedia enables sharing of human protein data. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:164–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

