A first-stage approximation to identify new imprinted genes through sequence analysis of its coding regions
- PMID: 19360135
- PMCID: PMC2666875
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/549387
A first-stage approximation to identify new imprinted genes through sequence analysis of its coding regions
Abstract
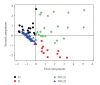
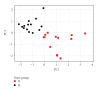
In the present study, a positive training set of 30 known human imprinted gene coding regions are compared with a set of 72 randomly sampled human nonimprinted gene coding regions (negative training set) to identify genomic features common to human imprinted genes. The most important feature of the present work is its ability to use multivariate analysis to look at variation, at coding region DNA level, among imprinted and non-imprinted genes. There is a force affecting genomic parameters that appears through the use of the appropriate multivariate methods (principle components analysis (PCA) and quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA)) to analyse quantitative genomic data. We show that variables, such as CG content, [bp]% CpG islands, [bp]% Large Tandem Repeats, and [bp]% Simple Repeats, are able to distinguish coding regions of human imprinted genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tandem repeats in the CpG islands of imprinted genes.Genomics. 2006 Sep;88(3):323-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.03.019. Epub 2006 May 11. Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16690248
-
Sequence conservation and variability of imprinting in the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome gene cluster in human and mouse.Hum Mol Genet. 2000 Jul 22;9(12):1829-41. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.12.1829. Hum Mol Genet. 2000. PMID: 10915772
-
Epigenetic profiling at mouse imprinted gene clusters reveals novel epigenetic and genetic features at differentially methylated regions.Genome Res. 2009 Aug;19(8):1374-83. doi: 10.1101/gr.089185.108. Epub 2009 Jun 19. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19542493 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic conflict, genomic imprinting and establishment of the epigenotype in relation to growth.Reproduction. 2001 Aug;122(2):185-93. doi: 10.1530/rep.0.1220185. Reproduction. 2001. PMID: 11467969 Review.
-
Imprinting of the mouse Igf2r gene depends on an intronic CpG island.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998 May 25;140(1-2):9-14. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(98)00022-7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9722161 Review.
Cited by
-
The application of restriction landmark genome scanning method for surveillance of non-mendelian inheritance in f(1) hybrids.Comp Funct Genomics. 2009;2009:245927. doi: 10.1155/2009/245927. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Comp Funct Genomics. 2009. PMID: 20148066 Free PMC article.
-
Differential decay of parent-of-origin-specific genomic sharing in cystic fibrosis-affected sib pairs maps a paternally imprinted locus to 7q34.Eur J Hum Genet. 2010 May;18(5):553-9. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2009.229. Epub 2010 Jan 6. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20051989 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinting of cerebral and hepatic cytochrome p450s in rat offsprings exposed prenatally to low doses of cypermethrin.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;48(1):128-40. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8419-5. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23447098
References
-
- Ohlsson R, Paldi A, Graves JAM. Did genomic imprinting and X chromosome inactivation arise from stochastic expression? Trends in Genetics. 2001;17(3):136–141. - PubMed
-
- Okamura K, Ito T. Lessons from comparative analysis of species-specific imprinted genes. Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 2006;113(1–4):159–164. - PubMed
-
- Neumann B, Kubicka P, Barlow DP. Characteristics of imprinted genes. Nature Genetics. 1995;9(1):12–13. - PubMed
-
- Shirohzu H, Yokomine T, Sato C, et al. A 210-kb segment of tandem repeats and retroelements located between imprinted subdomains of mouse distal chromosome 7. DNA Research. 2004;11(5):325–334. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources