A gamma-secretase inhibitor decreases amyloid-beta production in the central nervous system
- PMID: 19360898
- PMCID: PMC2730994
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.21623
A gamma-secretase inhibitor decreases amyloid-beta production in the central nervous system
Abstract
Objective: Accumulation of amyloid-beta (Abeta) by overproduction or underclearance in the central nervous system (CNS) is hypothesized to be a necessary event in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. However, previously, there has not been a method to determine drug effects on Abeta production or clearance in the human CNS. The objective of this study was to determine the effects of a gamma-secretase inhibitor on the production of Abeta in the human CNS.
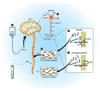
Methods: We utilized a recently developed method of stable-isotope labeling combined with cerebrospinal fluid sampling to directly measure Abeta production during treatment of a gamma-secretase inhibitor, LY450139. We assessed whether this drug could decrease CNS Abeta production in healthy men (age range, 21-50 years) at single oral doses of 100, 140, or 280mg (n = 5 per group).
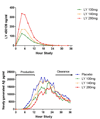
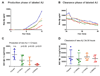
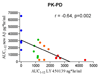
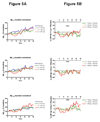
Results: LY450139 significantly decreased the production of CNS Abeta in a dose-dependent fashion, with inhibition of Abeta generation of 47, 52, and 84% over a 12-hour period with doses of 100, 140, and 280mg, respectively. There was no difference in Abeta clearance.
Interpretation: Stable isotope labeling of CNS proteins can be utilized to assess the effects of drugs on the production and clearance rates of proteins targeted as potential disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer's disease and other CNS disorders. Results from this approach can assist in making decisions about drug dosing and frequency in the design of larger and longer clinical trials for diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, and may accelerate effective drug validation. Ann Neurol 2009.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement: Drs. Bateman and Holtzman are co-founders of a company (C2N Diagnostics) which has licensed a pending Washington University patent on the technology described in this article. Drs. Siemers, Friedrich, Demattos, May and Paul are employees of Eli Lilly, the sponsor of this study.
Figures
Comment in
-
In response to "a gamma-secretase inhibitor decreases amyloid-beta production in the central nervous system".Ann Neurol. 2010 Jan;67(1):143-4; author reply 144-5. doi: 10.1002/ana.21929. Ann Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20186950 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bienias JL, et al. Alzheimer disease in the US population: prevalence estimates using the 2000 census. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:1119–1122. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H. Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 2006;368:387–403. - PubMed
-
- Skovronsky DM, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ. Neurodegenerative diseases: New concepts of pathogenesis and their therapeutic implications. Annual Review of Pathology. 2006;Vol. 1:151–170. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Golde TE, Dickson D, Hutton M. Filling the gaps in the Aβ cascade hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease. Current Alzheimer Research. 2006;3:421–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

