MicroRNA signatures in liver diseases
- PMID: 19360909
- PMCID: PMC2668771
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.1665
MicroRNA signatures in liver diseases
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are an emerging class of highly conserved non-coding small RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. It is now clear that miRNAs can potentially regulate every aspect of cellular activity, including differentiation and development, metabolism, proliferation, apoptotic cell death, viral infection and tumorigenesis. Recent studies provide clear evidence that miRNAs are abundant in the liver and modulate a diverse spectrum of liver functions. Deregulation of miRNA expression may be a key pathogenetic factor in many liver diseases including viral hepatitis, hepatocellular cancer and polycystic liver diseases. A clearer understanding of the mechanisms involved in miRNA deregulation will offer new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies to treat liver diseases. Moreover, better understanding of miRNA regulation and identification of tissue-specific miRNA targets employing transgenic/knockout models and/or modulating oligonucleotides will improve our knowledge of liver physiology and diseases.
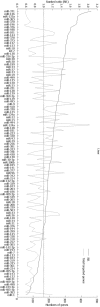
Figures


References
-
- Kiss T. Small nucleolar RNAs: an abundant group of noncoding RNAs with diverse cellular functions. Cell. 2002;109:145–148. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Voinnet O. Induction and suppression of RNA silencing: insights from viral infections. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:206–220. - PubMed
-
- Nelson P, Kiriakidou M, Sharma A, Maniataki E, Mourelatos Z. The microRNA world: small is mighty. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:534–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

