Bispectral index monitoring in ischemic-hypoxic brain injury
- PMID: 19361035
- PMCID: PMC4680226
Bispectral index monitoring in ischemic-hypoxic brain injury
Abstract
The BIS monitor is a simple-to-use and widely available monitor used in cardiac surgery. It can provide useful new information regarding the patient's hypnotic state, but also other components of brain function. The detection of cerebral hypoperfusion is of prime importance to perfusionists and others caring for patients undergoing cardiac surgery. BIS values consistent with the anesthetic drug and dose administration should reflect adequate cerebral perfusion and function. Abnormally low or a sudden deterioration in BIS values probably indicate cerebral hypoperfusion and should be taken seriously. A growing number of anecdotal reports and small case series support these contentions, but large prospective outcome studies are needed before this technology can be reliably used to monitor cerebral perfusion and other aspects of brain function during surgery.
Figures

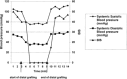
Similar articles
-
Artifact in the bispectral index in a patient with severe ischemic brain injury.Anesth Analg. 2004 Mar;98(3):706-7, table of contents. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000099360.49186.6b. Anesth Analg. 2004. PMID: 14980924
-
Perioperative cerebral ischaemia in cardiac surgery and BIS.Anaesth Intensive Care. 2005 Aug;33(4):514-7. doi: 10.1177/0310057X0503300415. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2005. PMID: 16119495
-
Changes in cerebral and somatic oxygenation during stage 1 palliation of hypoplastic left heart syndrome using continuous regional cerebral perfusion.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004 Jan;127(1):223-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.08.021. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004. PMID: 14752434
-
NIRS: a standard of care for CPB vs. an evolving standard for selective cerebral perfusion?J Extra Corpor Technol. 2009 Mar;41(1):P11-4. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2009. PMID: 19361034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Monitoring-Brain Function Monitoring and Cerebral Oximetry.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2019 Aug;33 Suppl 1:S53-S57. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2019.03.041. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2019. PMID: 31279353 Review.
Cited by
-
BiSpectral Index (BIS) monitoring may detect critical hypotension before automated non-invasive blood pressure (NIBP) measurement during general anaesthesia; a case report.F1000Res. 2014 Jan 9;3:5. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.3-5.v1. eCollection 2014. F1000Res. 2014. PMID: 25580217 Free PMC article.
-
Sedation management and processed EEG-based solutions during venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: a narrative review of key challenges and potential benefits.J Artif Organs. 2025 Sep;28(3):293-307. doi: 10.1007/s10047-025-01494-y. Epub 2025 Mar 8. J Artif Organs. 2025. PMID: 40056243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of baseline cognitive impairment on association between predicted propofol effect site concentration and Bispectral index or sedation score.BMC Anesthesiol. 2020 May 28;20(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-01043-5. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32466776 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The association of bispectral index values and metrics of cerebral perfusion during cardiopulmonary bypass.J Clin Anesth. 2021 Nov;74:110395. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2021.110395. Epub 2021 Jun 17. J Clin Anesth. 2021. PMID: 34147015 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in density spectral array of bilateral BIS during carotid external compression in cardiac surgery.J Clin Monit Comput. 2018 Dec;32(6):1147-1148. doi: 10.1007/s10877-018-0112-9. Epub 2018 Feb 14. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018. PMID: 29445904 No abstract available.
References
-
- Harukuni I, Bhardwaj A.. Mechanisms of brain injury after global cerebral ischemia. Neurol Clin. 2006;24:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Liou AK, Clark RS, Henshall DC, Yin XM, Chen J.. To die or not to die for neurons in ischemia, traumatic brain injury and epilepsy: A review on the stress-activated signaling pathways and apoptotic pathways. Prog Neurobiol. 2003;69:103–42. - PubMed
-
- Rampil I.. A primer for EEG signal processing in anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1998;89:980–1002. - PubMed
-
- Zandbergen EG, de Haan RJ, Stoutenbeek CP, Koelman JH, Hijdra A.. Systematic review of early prediction of poor outcome in anoxicischaemic coma. Lancet. 1998;352:1808–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
