Redox regulation of tumor necrosis factor signaling
- PMID: 19361274
- PMCID: PMC2819802
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2009.2611
Redox regulation of tumor necrosis factor signaling
Abstract
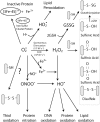
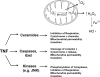
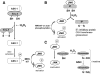
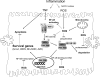
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) is a key cytokine that has been shown to play important physiologic (e.g., inflammation) and pathophysiologic (e.g., various liver pathologies) roles. In liver and other tissues, TNF treatment results in the simultaneous activation of an apoptotic pathway (i.e., TRADD, RIP, JNK) and a survival pathway mediated by NF-kappaB transcription of survival genes (i.e., GADD45beta, Mn-SOD, cFLIP). The cellular response (e.g., proliferation versus apoptosis) to TNF is determined by the balance between the apoptotic signaling pathway and the NF-kappaB survival pathway stimulated by TNF. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are important modulators of signaling pathways and can regulate both apoptotic signaling and NF-kappaB transcription triggered by TNF. ROS are important in mediating the sustained activation of JNK, to help mediate apoptosis after TNF treatment. In some cells, ROS are second messengers that mediate apoptosis after TNF stimulation. Conversely, ROS can cause redox modifications that inhibit NF-kappaB activation, which can lead to cell death triggered by TNF. Consequently, the redox status of cells can determine the biologic response that TNF will induce in cells. In many liver pathologies, ROS generated extrinsically (e.g., inflammation) or intrinsically (i.e., drugs, toxins) may act in concert with TNF to promote hepatocyte death and liver injury through redox inhibition of NF-kappaB.
Figures

References
-
- Antosiewicz J. Ziolkowski W. Kaczor JJ. Herman-Antosiewicz A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced reactive oxygen species formation is mediated by JNK1-dependent ferritin degradation and elevation of labile iron pool. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43:265–270. - PubMed
-
- Antras-Ferry J. Maheo K. Morel F. Guillouzo A. Cillard P. Cillard J. Dexamethasone differently modulates TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-induced transcription of the hepatic Mn-superoxide dismutase gene. FEBS Lett. 1997;403:100–104. - PubMed
-
- Antunes F. Han D. Cadenas E. Relative contributions of heart mitochondria glutathione peroxidase and catalase to H(2)O(2) detoxification in in vivo conditions. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;33:1260–1267. - PubMed
-
- Antunes F. Salvador A. Marinho HS. Alves R. Pinto RE. Lipid peroxidation in mitochondrial inner membranes, I: an integrative kinetic model. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996;21:917–943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

