Sequence-specific binding to a subset of IscR-regulated promoters does not require IscR Fe-S cluster ligation
- PMID: 19361432
- PMCID: PMC2709974
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.055
Sequence-specific binding to a subset of IscR-regulated promoters does not require IscR Fe-S cluster ligation
Abstract
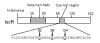
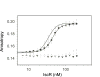
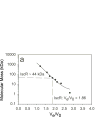
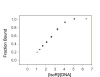
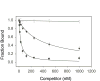
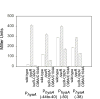
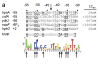
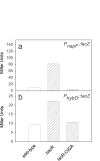
IscR is an Fe-S protein that functions as a transcriptional regulator of Fe-S biogenesis and other Fe-S protein-encoding genes in Escherichia coli. In this study, we investigated the requirement for the ligation of the [2Fe-2S] cluster of IscR to regulate a subset of IscR target promoters (P(hyaA), P(ydiU), P(napF), and P(hybO)) and defined the requirements for sequence-specific binding to the IscR target site in the hyaA promoter region. In contrast to previous results with the iscR promoter, we found that the Fe-S cluster is dispensable for IscR regulation of P(hyaA), P(ydiU), P(napF), and P(hybO), since IscR mutants containing alanine substitutions of the cysteine Fe-S ligands retained IscR-dependent regulation of these promoters in vivo. In vitro assays showed that both [2Fe-2S]-IscR and an IscR mutant lacking the cluster (IscR-C92A/C98A/C104A) bound the hya site with similar affinity, explaining why the mutant protein retained its ability to repress P(hyaA) in vivo. Characterization of the oligomeric state of IscR showed that both apo-IscR and [2Fe-2S]-IscR were dimers in solution, and four protomers of either form bound to the hya site. Also, binding of either apo- or [2Fe-2S]-IscR to the hya site showed cooperativity, suggesting that both forms interact similarly with the target site. Analysis of mutations in the hya site using DNA competition assays showed that apo-IscR most likely recognizes an imperfect palindrome within the hya promoter. Furthermore, the strength of apo-IscR binding to P(sufA), P(ydiU), P(napF), and P(hybO) IscR sites correlated with the number of matches to the hya site bases shown to be important in the competition assay. Thus, our data indicated that, unexpectedly, apo-IscR is a site-specific DNA-binding protein, and the role of apo-IscR needs to be considered in developing models for how IscR globally regulates transcription.
Figures



References
-
- Giel JL, Rodionov D, Liu M, Blattner FR, Kiley PJ. IscR-dependent gene expression links iron-sulphur cluster assembly to the control of O2-regulated genes in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 2006;60:1058–75. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DC, Dean DR, Smith AD, Johnson MK. Structure, function, and formation of biological iron-sulfur clusters. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:247–81. - PubMed
-
- Fontecave M, Ollagnier-de-Choudens S. Iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis in bacteria: Mechanisms of cluster assembly and transfer. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;474:226–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

