Disturbances in the secretion of neurotransmitters in IA-2/IA-2beta null mice: changes in behavior, learning and lifespan
- PMID: 19361477
- PMCID: PMC2672562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.01.022
Disturbances in the secretion of neurotransmitters in IA-2/IA-2beta null mice: changes in behavior, learning and lifespan
Abstract
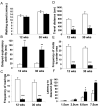
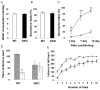
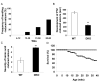
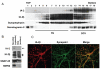
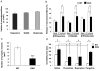
Islet-associated protein 2 (IA-2) and IA-2beta are major autoantigens in type 1 diabetes and transmembrane proteins in dense core secretory vesicles (DCV) of neuroendocrine cells. The deletion of these genes results in a decrease in insulin secretion. The present study was initiated to test the hypothesis that this deletion not only affects the secretion of insulin, but has a more global effect on neuroendocrine secretion that leads to disturbances in behavior and learning. Measurement of neurotransmitters showed that norepinephrine, dopamine and 5-HT were significantly decreased in the brain of double knockout (DKO) mice (P<0.05 to <0.001). In tests evaluating anxiety-like behavior and conditioned-learning, the DKO mice showed a highly significant increase in anxiety-like behavior (P<0.01 to <0.001) and impairment of conditioned learning (P<0.01) as compared to WT mice. The DKO mice also displayed an increase in spontaneous and induced seizures (P<0.01) and age-related death. Contrary to the generally held view that IA-2 and IA-2beta are expressed exclusively in DCV, subcellular fractionation studies revealed that IA-2beta, but not IA-2, co-purifies with fractions rich in synaptic vesicles (SV), and that the secretion of dopamine, GABA and glutamate from the synaptosomes of the DKO mice was significantly decreased as was the number of SV (P<0.01). Taken together, these findings show that IA-2beta is present in both DCV and SV, and that the deletion of IA-2/IA-2beta has a global effect on the secretion of neurotransmitters. The impairment of secretion leads to behavioral and learning disturbances, seizures and reduced lifespan.
Figures
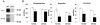
Similar articles
-
Pathophysiologic changes in IA-2/IA-2β null mice are secondary to alterations in the secretion of hormones and neurotransmitters.Acta Diabetol. 2016 Feb;53(1):7-12. doi: 10.1007/s00592-015-0750-z. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Acta Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 25861885 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Ia-2 and/or Ia-2β in mice decreases insulin secretion by reducing the number of dense core vesicles.Diabetologia. 2011 Sep;54(9):2347-57. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2221-6. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21732083 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the transmembrane dense core vesicle proteins IA-2 and IA-2beta causes female infertility.Endocrinology. 2006 Feb;147(2):811-5. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0638. Epub 2005 Nov 3. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16269463
-
IA-2 and IA-2beta: the immune response in IDDM.Diabetes Metab Rev. 1998 Mar;14(1):85-93. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0895(199803)14:1<85::aid-dmr205>3.0.co;2-i. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1998. PMID: 9605631 Review.
-
Expression and function of IA-2 family proteins, unique neuroendocrine-specific protein-tyrosine phosphatases.Endocr J. 2009;56(5):639-48. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.k09e-157. Epub 2009 Jun 24. Endocr J. 2009. PMID: 19550073 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiologic changes in IA-2/IA-2β null mice are secondary to alterations in the secretion of hormones and neurotransmitters.Acta Diabetol. 2016 Feb;53(1):7-12. doi: 10.1007/s00592-015-0750-z. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Acta Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 25861885 Free PMC article.
-
Strain-based and sex-biased differences in adrenal and pancreatic gene expression between KK/HlJ and C57BL/6 J mice.BMC Genomics. 2021 Mar 12;22(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07495-4. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33711921 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically-encoded markers for confocal visualization of single dense core vesicles.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 21:rs.3.rs-5021271. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5021271/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 07;8(1):383. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07829-y. PMID: 39502772 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The Ia-2β intronic miRNA, miR-153, is a negative regulator of insulin and dopamine secretion through its effect on the Cacna1c gene in mice.Diabetologia. 2015 Oct;58(10):2298-306. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3683-8. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 26141787 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Ubiquitin Ligase Adaptor PTPRN Suppresses Seizure Susceptibility through Endocytosis of NaV1.2 Sodium Channels.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(29):e2400560. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400560. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38874331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achenbach P, Bonifacio E, Williams AJ, Ziegler AG, Gale EA, Bingley PJ. Autoantibodies to IA-2beta improve diabetes risk assessment in high-risk relatives. Diabetologia. 2008;51:488–492. - PubMed
-
- Brennan PA, Schellinck HM, de la Riva C, Kendrick KM, Keverne EB. Changes in neurotransmitter release in the main olfactory bulb following an olfactory conditioning procedure in mice. Neuroscience. 1998;87:583–590. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Cagniard B, Mathews T, Jones S, Koh HC, Ding Y, Carvey PM, Ling Z, Kang UJ, Zhuang X. Age-dependent motor deficits and dopaminergic dysfunction in DJ-1 null mice. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:21418–21426. - PubMed
-
- Crawley JN. What's wrong with my mouse? : behavioral phenotyping of transgenic and knockout mice. Wiley-Liss; New York ; Chichester: 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

