Structural alterations within native amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chains
- PMID: 19361523
- PMCID: PMC2840394
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.010
Structural alterations within native amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chains
Abstract
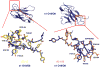
Amyloid diseases are characterized by the misfolding of a precursor protein that leads to amyloid fibril formation. Despite the fact that there are different precursors, some commonalities in the misfolding mechanism are thought to exist. In light chain amyloidosis (AL), the immunoglobulin light chain forms amyloid fibrils that deposit in the extracellular space of vital organs. AL proteins are thermodynamically destabilized compared to non-amyloidogenic proteins and some studies have linked this instability to increased fibril formation rates. Here we present the crystal structures of two highly homologous AL proteins, AL-12 and AL-103. This structural study shows that these proteins retain the canonical germ line dimer interface. We highlight important structural alterations in two loops flanking the dimer interface and correlate these results with the somatic mutations present in AL-12 and AL-103. We suggest that these alterations are informative structural features that are likely contributing to protein instability that leads to conformational changes involved in the initial events of amyloid formation.
Figures
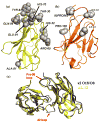
Similar articles
-
Mutations can cause light chains to be too stable or too unstable to form amyloid fibrils.Protein Sci. 2015 Nov;24(11):1829-40. doi: 10.1002/pro.2790. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 26300552 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-induced native dimerization prevents amyloid formation by variable domain from immunoglobulin light-chain REI.FEBS J. 2017 Sep;284(18):3114-3127. doi: 10.1111/febs.14181. Epub 2017 Aug 13. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28736891
-
Mutations in specific structural regions of immunoglobulin light chains are associated with free light chain levels in patients with AL amyloidosis.PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005169. Epub 2009 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19365555 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin light chain amyloid aggregation.Chem Commun (Camb). 2018 Sep 20;54(76):10664-10674. doi: 10.1039/c8cc04396e. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018. PMID: 30087961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards understanding the structure-function relationship of human amyloid disease.Curr Drug Targets. 2004 Feb;5(2):159-71. doi: 10.2174/1389450043490550. Curr Drug Targets. 2004. PMID: 15011949 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations can cause light chains to be too stable or too unstable to form amyloid fibrils.Protein Sci. 2015 Nov;24(11):1829-40. doi: 10.1002/pro.2790. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 26300552 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Doppler myocardial imaging, cardiac biomarkers, and clonal immunoglobulin genes to assess left ventricular performance and stratify risk following peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in patients with systemic light chain amyloidosis (Al).J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011 Apr;24(4):444-54. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2011.01.003. Epub 2011 Feb 18. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011. PMID: 21315556 Free PMC article.
-
Site-directed mutagenesis reveals regions implicated in the stability and fiber formation of human λ3r light chains.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 30;290(5):2577-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.629550. Epub 2014 Dec 11. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25505244 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosaminoglycans promote fibril formation by amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chains through a transient interaction.Biophys Chem. 2011 Sep;158(1):81-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 18. Biophys Chem. 2011. PMID: 21640469 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Insights into the Early Events in the Aggregation of Immunoglobulin Light Chains.Biochemistry. 2019 Jul 23;58(29):3155-3168. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00311. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31287666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dobson CM. Protein misfolding, evolution and disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:329–332. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez-Alvarado M, De Stigter JK, Baden EM, Sikkink LA, McLaughlin RW, Taboas AL. Immunoglobulin Light Chain and Systemic Light-Chain Amyloidosis. In: Uversky VN, Fink AL, editors. Protein Misfolding, Aggregation, and Conformational Diseases, Part B: Molecular Mechanisms of Conformational Diseases. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC; New York: 2007. pp. 183–197.
-
- Solomon A, Weiss DT. Protein and host factors implicated in the pathogenesis of light chain amyloidosis (AL amyloidosis) Amyloid: Int J Exp Clin Invest. 1995;2:269–279.
-
- Comenzo RL, Wally J, Kica G, Murray J, Ericsson T, Skinner M, Zhang Y. Clonal immunoglobulin light chain variable region germline gene use in AL amyloidosis: association with dominant amyloid-related organ involvement and survival after stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol. 1999;106:744–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

