Stress exacerbates neuropathic pain via glucocorticoid and NMDA receptor activation
- PMID: 19361551
- PMCID: PMC2735409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2009.04.001
Stress exacerbates neuropathic pain via glucocorticoid and NMDA receptor activation
Abstract
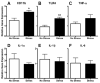
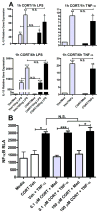
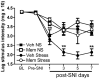
There is growing recognition that psychological stress influences pain. Hormones that comprise the physiological response to stress (e.g., corticosterone; CORT) may interact with effectors of neuropathic pain. To test this hypothesis, mice received a spared nerve injury (SNI) after exposure to 60 min restraint stress. In stressed mice, allodynia was consistently increased. The mechanism(s) underlying the exacerbated pain response involves CORT acting via glucocorticoid receptors (GRs); RU486, a GR antagonist, prevented the stress-induced increase in allodynia whereas exogenous administration of CORT to non-stressed mice reproduced the allodynic response caused by stress. Since nerve injury-induced microglial activation has been implicated in the onset and propagation of neuropathic pain, we evaluated cellular and molecular indices of microglial activation in the context of stress. Activation of dorsal horn microglia was accelerated by stress; however, this effect was transient and was not associated with the onset or maintenance of a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Stress-enhanced allodynia was associated with increased dorsal horn extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation (pERK). ERK activation could indicate a stress-mediated increase in glutamatergic signaling, therefore mice were treated prior to SNI and stress with memantine, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist. Memantine prevented stress-induced enhancement of allodynia after SNI. These data suggest that the hormonal responses elicited by stress exacerbate neuropathic pain through enhanced central sensitization. Moreover, drugs that inhibit glucocorticoids (GCs) and/or NMDAR signaling could ameliorate pain syndromes caused by stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest pertaining to the data described herein.
Figures
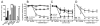


References
-
- Ashkinazi I, Vershinina EA. Pain sensitivity in chronic psychoemotional stress in humans. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 1999;29:333–7. - PubMed
-
- Binns BC, Huang Y, Goettl VM, Hackshaw KV, Stephens RL., Jr Glutamate uptake is attenuated in spinal deep dorsal and ventral horn in the rat spinal nerve ligation model. Brain Res. 2005;1041:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn-Munro G, Blackburn-Munro R. Pain in the brain: are hormones to blame? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003;14:20–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

