Lipophilicity of potent porphyrin-based antioxidants: comparison of ortho and meta isomers of Mn(III) N-alkylpyridylporphyrins
- PMID: 19361553
- PMCID: PMC2694496
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.04.002
Lipophilicity of potent porphyrin-based antioxidants: comparison of ortho and meta isomers of Mn(III) N-alkylpyridylporphyrins
Abstract
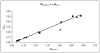
Mn(III) N-alkylpyridylporphyrins are among the most potent known SOD mimics and catalytic peroxynitrite scavengers and modulators of redox-based cellular transcriptional activity. In addition to their intrinsic antioxidant capacity, bioavailability plays a major role in their in vivo efficacy. Although of identical antioxidant capacity, lipophilic MnTnHex-2-PyP is up to 120-fold more efficient in reducing oxidative stress injuries than hydrophilic MnTE-2-PyP. Owing to limitations of an analytical nature, porphyrin lipophilicity has been often estimated by the thin-layer chromatographic R(f) parameter, instead of the standard n-octanol/water partition coefficient, P(OW). Herein we used a new methodological approach to finally describe the MnP lipophilicity, using the conventional log P(OW) means, for a series of biologically active ortho and meta isomers of Mn(III) N-alkylpyridylporphyrins. Three new porphyrins (MnTnBu-3-PyP, MnTnHex-3-PyP, and MnTnHep-2-PyP) were synthesized to strengthen the conclusions. The log P(OW) was linearly related to R(f) and to the number of carbons in the alkyl chain (n(C)) for both isomer series, the meta isomers being 10-fold more lipophilic than the analogous ortho porphyrins. Increasing the length of the alkyl chain by one carbon atom increases the log P(OW) value approximately 1 log unit with both isomers. Dramatic approximately 4 and approximately 5 orders of magnitude increases in the lipophilicity of the ortho isomers, by extending the pyridyl alkyl chains from two (MnTE-2-PyP, log P(OW)=-6.89) to six (MnTnHex-2-PyP, log P(OW)=-2.76) and eight carbon atoms (MnTnOct-2-PyP, log P(OW)=-1.24), parallels the increased efficacy in several oxidative-stress injury models, particularly those of the central nervous system, in which transport across the blood-brain barrier is critical. Although meta isomers are only slightly less potent SOD mimics and antioxidants than their ortho analogues, their higher lipophilicity and smaller bulkiness may lead to a higher cellular uptake and overall similar effectiveness in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 4. Biosciences; Oxford: 2007.
-
- Van Empel VPM, Bertrand AT, Van Oort RJ, Van der Nagel R, Engelen M, Van Rijen HV, Doevendans PA, Crijns HJ, Ackerman SL, Sluiter W, De Windt LJ. EUK-8, a superoxide dismutase and catalase mimetic, reduces cardiac oxidative stress and ameliorates pressure overload-induced heart failure in the harlequin mouse mutant. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:8245–832. - PubMed
-
- Salvemini D, Wang Z-Q, Zweier JL, Samouilov A, Macarthur H, Misko TP, Curie MG, Cuzzocrea S, Sikorski JA, Riley DP. A nonpeptidyl mimic of superoxide dismutase with therapeutic activity ion rats. Science. 1999;286:304–306. - PubMed
-
- Batinic-Haberle I, Benov L, Spasojevic I, Hambright P, Crumbliss AL, Fridovich I. The Relationship Between Redox Potentials, Proton Dissociation Constants of Pyrrolic Nitrogens, and in Vitro and in Vivo Superoxide Dismutase Activities of Manganese(III) and Iron(III) Cationic and Anionic Porphyrins. Inorg Chem. 1999;38:4011–4022.
-
- Goldstein S, Samuni A, Hideg K, Merenyi G. Structure-activity relationship of cyclic nitroxides as SOD mimics and scavengers of nitrogen dioxide and carbonate radicals. J Phys Chem A. 2006;110:3679–3685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

