Cell death mechanisms in GT1-7 GnRH cells exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls PCB74, PCB118, and PCB153
- PMID: 19362103
- PMCID: PMC2702519
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.04.001
Cell death mechanisms in GT1-7 GnRH cells exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls PCB74, PCB118, and PCB153
Abstract
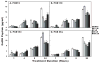
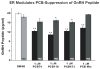
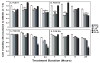
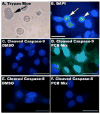
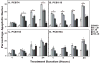
Exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) causes functional deficits in neuroendocrine systems. We used an immortalized hypothalamic GT1-7 cell line, which synthesizes the neuroendocrine peptide gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), to examine the neurotoxic and endocrine disrupting effects of PCBs and their mechanisms of action. Cells were treated for 1, 4, 8, or 24 h with a range of doses of a representative PCB from each of three classes: coplanar (2,4,4',5-tetrachlorobiphenyl: PCB74), dioxin-like coplanar (2',3,4,4',5' pentachlorobiphenyl: PCB118), non-coplanar (2,2',4,4',5,5'-hexachlorobiphenyl: PCB153), or their combination. GnRH peptide concentrations, cell viability, apoptotic and necrotic cell death, and caspase activation were quantified. In general, GnRH peptide levels were suppressed by high doses and longer durations of PCBs, and elevated at low doses and shorter timepoints. The suppression of GnRH peptide levels was partially reversed in cultures co-treated with the estrogen receptor antagonist ICI 182,780. All PCBs reduced viability and increased both apoptotic and necrotic cell death. Although the effects for the three classes of PCBs were often similar, subtle differences in responses, together with evidence that the combination of PCBs acted slightly different from individual PCBs, suggest that the three tested PCB compounds may act via slightly different or more than one mechanism. These results provide evidence that PCB congeners have endocrine disrupting and/or neurotoxic effects on the hypothalamic GnRH cell line, a finding that has implications for environmental endocrine disruption in animals.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

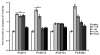
Similar articles
-
A novel mechanism for endocrine-disrupting effects of polychlorinated biphenyls: direct effects on gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurones.J Neuroendocrinol. 2002 Oct;14(10):814-23. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2826.2002.00845.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12372006
-
NTP technical report on the toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of 2,2',4,4',5,5'-hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB 153) (CAS No. 35065-27-1) in female Harlan Sprague-Dawley rats (Gavage studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2006 May;(529):4-168. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2006. PMID: 16835634
-
Estrogenic environmental endocrine-disrupting chemical effects on reproductive neuroendocrine function and dysfunction across the life cycle.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2007 Jun;8(2):143-59. doi: 10.1007/s11154-007-9048-y. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2007. PMID: 17674209 Review.
-
Hippocampal neurons exposed to the environmental contaminants methylmercury and polychlorinated biphenyls undergo cell death via parallel activation of calpains and lysosomal proteases.Neurotox Res. 2011 Jan;19(1):183-94. doi: 10.1007/s12640-010-9159-1. Epub 2010 Feb 19. Neurotox Res. 2011. PMID: 20169435
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implications for risk assessment.Crit Rev Toxicol. 1994;24(2):87-149. doi: 10.3109/10408449409049308. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1994. PMID: 8037844 Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal PCBs disrupt early neuroendocrine development of the rat hypothalamus.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 1;252(1):36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2011.01.012. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21277884 Free PMC article.
-
Interference with Systemic Negative Feedback Regulation as a Potential Mechanism for Nonmonotonic Dose-Responses of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 8:2024.09.04.611257. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.04.611257. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Toxicol Sci. 2025 Aug 01;206(2):354-372. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaf060. PMID: 39282254 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Neuroendocrine targets of endocrine disruptors.Hormones (Athens). 2010 Jan-Mar;9(1):16-27. doi: 10.14310/horm.2002.1249. Hormones (Athens). 2010. PMID: 20363718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of cell viability, oxidative stress, calcium homeostasis, and voltage- and ligand-gated ion channels as common mechanisms of action of (mixtures of) non-dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014 May;21(10):6373-83. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1759-x. Epub 2013 May 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014. PMID: 23686757 Review.
-
Endocrine-disrupting actions of PCBs on brain development and social and reproductive behaviors.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;19:134-44. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2014.09.020. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25310366 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altmann L, Mundy WR, Ward TR, Fastabend A, Lilienthal H. Developmental exposure of rats to a reconstituted PCB mixture or Aroclor 1254: effects on long-term potentiation and [3H]MK-801 binding in occipital cortex and hippocampus. Toxicol Sci. 2001;61:321–330. - PubMed
-
- Bonefeld-Jørgensen EC, Andersen HR, Rasmussen TH, Vinggaard AM. Effect of highly bioaccumulated polychlorinated biphenyl congeners on estrogen and androgen receptor activity. Toxicology. 2001;158:141–153. - PubMed
-
- Coccini T, Randine G, Castoldi AF, Grandjean P, Ostendorp G, Heinzow B, Manzo L. Effects of developmental co-exposure to methylmercury and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB153) on cholinergic muscarinic receptors in rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 2006;27:468–477. - PubMed
-
- Costa LG, Fattori V, Giordano G, Vitalone A. An in vitro approach to assess the toxicity of certain food contaminants: methylmercury and polychlorinated biphenyls. Toxicology. 2007;237:65–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

