Association of botulinum neurotoxins with synaptic vesicle protein complexes
- PMID: 19362106
- PMCID: PMC2730980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.01.040
Association of botulinum neurotoxins with synaptic vesicle protein complexes
Abstract
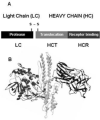
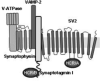
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) elicit flaccid paralysis by cleaving SNARE proteins within peripheral neurons. BoNTs are classified into seven serotypes, termed A-G, based on antibody cross-neutralization. Clostridia produce BoNTs as single-chain toxins that are cleaved into a di-chain protein that comprises an N-terminal zinc metalloprotease domain that is linked by a disulfide bond to the C-terminal translocation/receptor-binding domain. BoNT/A and BoNT/B utilize synaptic vesicle protein 2 (SV2) and synaptotagmin, respectively, as receptors for entry into neurons. Using affinity chromatography, BoNT/A and BoNT/B were found to bind a synaptic vesicle protein complex in CHAPS extracts of synaptic vesicles. Mass spectroscopy identified synaptic vesicle protein 2, synaptotagmin I, synaptophysin, vesicle-associated membrane protein 2, and the vacuolar ATPase-proton pump as components of the BoNT-synaptic vesicle protein complex. BoNT/A and BoNT/B possessed unique density-gradient profiles when bound to synaptic vesicle protein complexes. The identification of BoNT/A and BoNT/B bound to synaptic vesicle protein complexes provides insight into the interactions of BoNT and neuronal receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Baldwin MR, Barbieri JT. Association of botulinum neurotoxin serotypes a and B with synaptic vesicle protein complexes. Biochemistry. 2007;46:3200–3210. - PubMed
-
- Belizaire R, Komanduri C, Wooten K, Chen M, Thaller C, Janz R. Characterization of synaptogyrin 3 as a new synaptic vesicle protein. J Comp Neurol. 2004;470:266–281. - PubMed
-
- Blasi J, Chapman ER, Link E, Binz T, Yamasaki S, De Camilli P, Sudhof TC, Niemann H, Jahn R. Botulinum neurotoxin A selectively cleaves the synaptic protein SNAP-25. Nature. 1993a;365:160–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

