Serine palmitoyltransferase subunit 1 is present in the endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus and focal adhesions, and functions in cell morphology
- PMID: 19362163
- PMCID: PMC2801055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.03.016
Serine palmitoyltransferase subunit 1 is present in the endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus and focal adhesions, and functions in cell morphology
Abstract
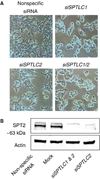
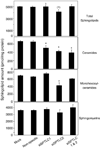
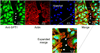
Serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) has been localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by subcellular fractionation and enzymatic assays, and fluorescence microscopy of epitope-tagged SPT; however, our studies have suggested that SPT subunit 1 might be present also in focal adhesions and the nucleus. These additional locations have been confirmed by confocal microscopy using HEK293 and HeLa cells, and for focal adhesions by the demonstration that SPT1 co-immunoprecipitates with vinculin, a focal adhesion marker protein. The focal adhesion localization of SPT1 is associated with cell morphology, and possibly cell migration, because it is seen in most cells before they reach confluence but disappears when they become confluent, and is restored by a standard scratch-wound healing assay. Conversely, elimination of SPT1 using SPTLC1 siRNA causes cell rounding. Thus, in addition to its "traditional" localization in the ER for de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis, SPT1 is present in other cellular compartments, including focal adhesions where it is associated with cell morphology.
Figures







References
-
- Alvarez SE, Milstien S, Spiegel S. Autocrine and paracrine roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2007;18:300–307. - PubMed
-
- Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. 2008;9:139–150. - PubMed
-
- Merrill AH, Jr, Wang MD, Park M, Sullards MC. (Glyco)sphingolipidology: an amazing challenge and opportunity for systems biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007;32:457–468. - PubMed
-
- Spiegel S, Milstien S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat. Rev. 2003;4:397–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

