Vascular injury after whole thoracic x-ray irradiation in the rat
- PMID: 19362237
- PMCID: PMC2745917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.01.006
Vascular injury after whole thoracic x-ray irradiation in the rat
Abstract
Purpose: To study vascular injury after whole thoracic irradiation with single sublethal doses of X-rays in the rat and to develop markers that might predict the severity of injury.
Methods and materials: Rats that received 5- or 10-Gy thorax-only irradiation and age-matched controls were studied at 3 days, 2 weeks, and 1, 2, 5, and 12 months. Several pulmonary vascular parameters were evaluated, including hemodynamics, vessel density, total lung angiotensin-converting enzyme activity, and right ventricular hypertrophy.
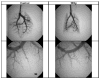
Results: By 1 month, the rats in the 10-Gy group had pulmonary vascular dropout, right ventricular hypertrophy, increased pulmonary vascular resistance, increased dry lung weights, and decreases in total lung angiotensin-converting enzyme activity, as well as pulmonary artery distensibility. In contrast, irradiation with 5 Gy resulted in only a modest increase in right ventricular weight and a reduction in lung angiotensin-converting enzyme activity.
Conclusion: In a previous investigation using the same model, we observed that recovery from radiation-induced attenuation of pulmonary vascular reactivity occurred. In the present study, we report that deterioration results in several vascular parameters for </=1 year after 10 Gy, suggesting sustained remodeling of the pulmonary vasculature. Our data support clinically relevant injuries that appear in a time- and dose-related manner after exposure to relatively low radiation doses.
Figures
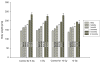

 /τ/ξ/γ p ≤ 0.02 vs age-matched controls).
/τ/ξ/γ p ≤ 0.02 vs age-matched controls).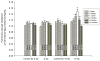



 /^/</# p ≤ 0.02 vs age-matched controls).
/^/</# p ≤ 0.02 vs age-matched controls).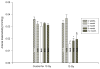
Similar articles
-
Structural and functional alterations in the rat lung following whole thoracic irradiation with moderate doses: injury and recovery.Int J Radiat Biol. 2008 Jun;84(6):487-97. doi: 10.1080/09553000802078396. Int J Radiat Biol. 2008. PMID: 18470747 Free PMC article.
-
Renin-Angiotensin system suppression mitigates experimental radiation pneumonitis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Dec 1;75(5):1528-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1743. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 19931735 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of radiation induced pulmonary vascular injury by delayed treatment with captopril.Respirology. 2012 Nov;17(8):1261-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2012.02247.x. Respirology. 2012. PMID: 22882664 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Radiation-induced Lung Injury in the Non-human Primate: A Review and Comparison of Mortality and Co-morbidities Using Models of Partial-body Irradiation with Marginal Bone Marrow Sparing and Whole Thorax Lung Irradiation.Health Phys. 2020 Nov;119(5):559-587. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001346. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 33009295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation damage to the lung: mitigation by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.Respirology. 2012 Jan;17(1):66-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02092.x. Respirology. 2012. PMID: 22023053 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Model development and use of ACE inhibitors for preclinical mitigation of radiation-induced injury to multiple organs.Radiat Res. 2014 Nov;182(5):545-55. doi: 10.1667/RR13425.1. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 25361399 Free PMC article.
-
Enalapril mitigates focal alveolar lesions, a histological marker of late pulmonary injury by radiation to the lung.Radiat Res. 2013 Apr;179(4):465-74. doi: 10.1667/RR3127.1. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Radiat Res. 2013. PMID: 23480564 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling and multiscale characterization of the quantitative imaging based fibrosis index reveals pathophysiological, transcriptome and proteomic correlates of lung fibrosis induced by fractionated irradiation.Int J Cancer. 2019 Jun 15;144(12):3160-3173. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32059. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30536712 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting radiation-induced injury using rapid 3D variogram analysis of CT images of rat lungs.Acad Radiol. 2013 Oct;20(10):1264-71. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2013.07.001. Acad Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24029058 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-thorax irradiation induces hypoxic respiratory failure, pleural effusions and cardiac remodeling.J Radiat Res. 2015 Mar;56(2):248-60. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rru095. Epub 2014 Nov 3. J Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 25368342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coleman CN, Blakely WF, Fike JR, et al. Molecular and cellular biology of moderate-dose (1–10 Gy) radiation and potential mechanisms of radiation protection: Report of a workshop at Bethesda, Maryland, December 17–18, 2001. Radiat Res. 2003;59:812–834. - PubMed
-
- Bentzen SM. Preventing or reducing late side effects of radiation therapy: radiobiology meets molecular pathology. Nature. 2006;6:702–713. - PubMed
-
- Law MP. Radiation induced vascular injury and its relation to late effects in normal tissues. Adv Radiat Biol. 1981;9:37–73.
-
- Shinohara S, Arikawa K. Radioisotopic Assessment on Development of Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis. Australas Radiol. 1972;6:363–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

