Plasma endothelin-1 level at the onset of ischemic ventricular fibrillation predicts resuscitation outcome
- PMID: 19362407
- PMCID: PMC2677120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2009.02.004
Plasma endothelin-1 level at the onset of ischemic ventricular fibrillation predicts resuscitation outcome
Abstract
Background: Endogenous vasopressors, including endothelin-1 (ET-1), have been shown to be elevated in patients following resuscitation from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and are likely a physiologic response to global ischaemia. The importance of ET-1 in the setting of arrest and resuscitation has not been established. Prior work has demonstrated that ET-1 increases significantly after coronary occlusion. The purpose of this study was to assess changes in ET-1 following induction of ischaemia and VF.
Methods: VF was induced in 30 anesthetized and instrumented swine by balloon occlusion of the LAD. Blood was collected from the right atrium at baseline and at 5 min intervals following LAD occlusion until VF occurred. After 7 min of VF, resuscitation was attempted in accordance with guidelines. ET-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), a measure of infarct size, were measured using ELISA.
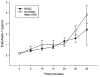
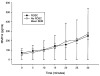
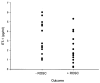
Results: ET-1 and MMP-9 levels increased significantly from baseline within 20 min of occlusion of the LAD. Animals that could not be resuscitated had a higher ET-1 (p=0.031) at VF onset but similar ischaemia time (time to VF) and MMP-9, reflecting infarct size. An ET-1 level >4 pg/ml had a likelihood ratio of 4 for predicting resuscitation failure.
Conclusions: Elevated levels of ET-1 during acute ischaemia predict resuscitation failure independent of the time to VF. This finding may be due to the known effect of ET-1 on coronary vascular resistance or ventricular compliance, resulting in early ischemic contracture.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelin-1 attenuates the hemodynamic response to exogenous epinephrine in a porcine ischemic ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest model.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Sep;31(9):679-84. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0012. Epub 2011 Jun 8. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21651344 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 is not predictive of ventricular ectopy or ventricular fibrillation during acute myocardial ischemia.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008 Nov;28(11):639-41. doi: 10.1089/jir.2008.0026. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008. PMID: 18844577 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial effects of ventricular fibrillation in the isolated rat heart.Crit Care Med. 1999 Aug;27(8):1542-50. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199908000-00023. Crit Care Med. 1999. PMID: 10470762
-
Sodium nitroprusside enhanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation improves short term survival in a porcine model of ischemic refractory ventricular fibrillation.Resuscitation. 2017 Jan;110:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2016.09.032. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Resuscitation. 2017. PMID: 27771299 Free PMC article.
-
The proinflammatory cytokine response following resuscitation in the swine model depends on the method of ventricular fibrillation induction.Acad Emerg Med. 2008 Oct;15(10):939-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2008.00237.x. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Acad Emerg Med. 2008. PMID: 18785945 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Endothelin-1 attenuates the hemodynamic response to exogenous epinephrine in a porcine ischemic ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest model.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Sep;31(9):679-84. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0012. Epub 2011 Jun 8. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21651344 Free PMC article.
-
High Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor Levels in the Early Post-Cardiac Arrest Period Are Associated with Poor Short-Term Survival in a Swine Model of Ventricular Fibrillation.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016 Oct;36(10):575-579. doi: 10.1089/jir.2016.0028. Epub 2016 Sep 8. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016. PMID: 27607559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brunner F, Bras-Silva C, Cerdeira AS, Leite-Moreira AF. Cardiovascular endothelins: essential regulators of cardiovascular homeostasis. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;111:508–531. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz-Spanke S, Schipke JD. Potential role of endothelin-1 and endothelin antagonists in cardiovascular disease. Basic Res Cardiol. 2000;95:290–298. - PubMed
-
- Pernow J, Wang Q. Endothelin in myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion. Cardiovas Res. 1997;33:518–526. - PubMed
-
- Cernacek P, Stewart DJ, Mange J, Rouleau J. The endothelin system and its role in acute myocardial infarction. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003;81:598–606. - PubMed
-
- Magder S, Cernacek P. Role of endothelins in septic, cardiogenic, and hemorrhagic shock. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003;81:635–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

