Genetic architecture of tameness in a rat model of animal domestication
- PMID: 19363126
- PMCID: PMC2691762
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.102186
Genetic architecture of tameness in a rat model of animal domestication
Abstract
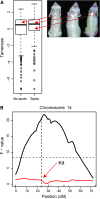
A common feature of domestic animals is tameness-i.e., they tolerate and are unafraid of human presence and handling. To gain insight into the genetic basis of tameness and aggression, we studied an intercross between two lines of rats (Rattus norvegicus) selected over >60 generations for increased tameness and increased aggression against humans, respectively. We measured 45 traits, including tameness and aggression, anxiety-related traits, organ weights, and levels of serum components in >700 rats from an intercross population. Using 201 genetic markers, we identified two significant quantitative trait loci (QTL) for tameness. These loci overlap with QTL for adrenal gland weight and for anxiety-related traits and are part of a five-locus epistatic network influencing tameness. An additional QTL influences the occurrence of white coat spots, but shows no significant effect on tameness. The loci described here are important starting points for finding the genes that cause tameness in these rats and potentially in domestic animals in general.
Figures
References
-
- Albert, F. W., O. Shchepina, C. Winter, H. Römpler, D. Teupser et al., 2008. Phenotypic differences in behavior, physiology and neurochemistry between rats selected for tameness and for defensive aggression towards humans. Horm. Behav. 53 413–421. - PubMed
-
- Bates, D., 2007. lme4: Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using S4 Classes. R package version 0.99875–9. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lme4/index.html.
-
- Belyaev, D. K., and P. M. Borodin, 1982. The influence of stress on variation and its role in evolution. Biol. Zent. Bl. 100 705–714.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

