Beta-arrestin-dependent signaling and trafficking of 7-transmembrane receptors is reciprocally regulated by the deubiquitinase USP33 and the E3 ligase Mdm2
- PMID: 19363159
- PMCID: PMC2667797
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0901083106
Beta-arrestin-dependent signaling and trafficking of 7-transmembrane receptors is reciprocally regulated by the deubiquitinase USP33 and the E3 ligase Mdm2
Abstract
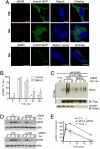
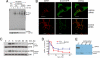
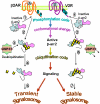
Beta-arrestins are multifunctional adaptors that mediate the desensitization, internalization, and some signaling functions of seven-transmembrane receptors (7TMRs). Agonist-stimulated ubiquitination of beta-arrestin2 mediated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Mdm2 is critical for rapid beta(2)-adrenergic receptor (beta(2)AR) internalization. We now report the discovery that the deubiquitinating enzyme ubiquitin-specific protease 33 (USP33) binds beta-arrestin2 and leads to the deubiquitination of beta-arrestins. USP33 and Mdm2 function reciprocally and favor respectively the stability or lability of the receptor beta-arrestin complex, thus regulating the longevity and subcellular localization of receptor signalosomes. Receptors such as the beta(2)AR, previously shown to form loose complexes with beta-arrestin ("class A") promote a beta-arrestin conformation conducive for binding to the deubiquitinase, whereas the vasopressin V2R, which forms tight beta-arrestin complexes ("class B"), promotes a distinct beta-arrestin conformation that favors dissociation of the enzyme. Thus, USP33-beta-arrestin interaction is a key regulatory step in 7TMR trafficking and signal transmission from the activated receptors to downstream effectors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
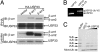


References
-
- Drake MT, Shenoy SK, Lefkowitz RJ. Trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors. Circ Res. 2006;99:570–582. - PubMed
-
- DeWire SM, Ahn S, Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK. Beta-arrestins and cell signaling. Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;69:483–510. - PubMed
-
- Oakley RH, et al. Differential affinities of visual arrestin, beta arrestin1, and beta arrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:17201–17210. - PubMed
-
- Shenoy SK, McDonald PH, Kohout TA, Lefkowitz RJ. Regulation of receptor fate by ubiquitination of activated beta 2-adrenergic receptor and beta-arrestin. Science. 2001;294:1307–1313. - PubMed
-
- Shenoy SK, Lefkowitz RJ. Trafficking patterns of beta-arrestin and G protein-coupled receptors determined by the kinetics of beta-arrestin deubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:14498–14506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

