Expression of the ggpPS gene for glucosylglycerol biosynthesis from Azotobacter vinelandii improves the salt tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 19363207
- PMCID: PMC2671616
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erp030
Expression of the ggpPS gene for glucosylglycerol biosynthesis from Azotobacter vinelandii improves the salt tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
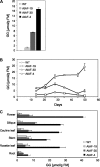
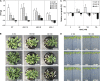
Many organisms accumulate compatible solutes in response to salt or desiccation stress. Moderate halotolerant cyanobacteria and some heterotrophic bacteria synthesize the compatible solute glucosylglycerol (GG) as their main protective compound. In order to analyse the potential of GG to improve salt tolerance of higher plants, the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana was transformed with the ggpPS gene from the gamma-proteobacterium Azotobacter vinelandii coding for a combined GG-phosphate synthase/phosphatase. The heterologous expression of the ggpPS gene led to the accumulation of high amounts of GG. Three independent Arabidopsis lines showing different GG contents were characterized in growth experiments. Plants containing a low (1-2 micromol g(-1) FM) GG content in leaves showed no altered growth performance under control conditions but an increased salt tolerance, whereas plants accumulating a moderate (2-8 micromol g(-1) FM) or a high GG content (around 17 micromol g(-1) FM) showed growth retardation and no improvement of salt resistance. These results indicate that the synthesis of the compatible solute GG has a beneficial effect on plant stress tolerance as long as it is accumulated to an extent that does not negatively interfere with plant metabolism.
Figures
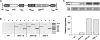


Similar articles
-
The plant-associated bacterium Stenotrophomonas rhizophila expresses a new enzyme for the synthesis of the compatible solute glucosylglycerol.J Bacteriol. 2008 Sep;190(17):5898-906. doi: 10.1128/JB.00643-08. Epub 2008 Jun 27. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18586931 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-dependent expression of glucosylglycerol-phosphate synthase, involved in osmolyte synthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803.J Bacteriol. 2002 Jun;184(11):2870-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.11.2870-2877.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12003926 Free PMC article.
-
The gene ssl3076 encodes a protein mediating the salt-induced expression of ggpS for the biosynthesis of the compatible solute glucosylglycerol in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803.J Bacteriol. 2010 Sep;192(17):4403-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.00481-10. Epub 2010 Jul 2. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20601470 Free PMC article.
-
Compatible solute biosynthesis in cyanobacteria.Environ Microbiol. 2011 Mar;13(3):551-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02366.x. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21054739 Review.
-
Salt-Regulated Accumulation of the Compatible Solutes Sucrose and Glucosylglycerol in Cyanobacteria and Its Biotechnological Potential.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 13;10:2139. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02139. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31572343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ABC-type salt tolerance transporter genes are abundant and mutually shared among the microorganisms of the hypersaline Sambhar Lake.Extremophiles. 2025 Jan 28;29(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s00792-025-01378-2. Extremophiles. 2025. PMID: 39873828
-
Isolation of gene conferring salt tolerance from halophilic bacteria of Lunsu, Himachal Pradesh, India.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2020 Oct 6;18(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s43141-020-00070-6. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33025336 Free PMC article.
-
Salt acclimation of cyanobacteria and their application in biotechnology.Life (Basel). 2014 Dec 29;5(1):25-49. doi: 10.3390/life5010025. Life (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25551682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional metagenomics identifies novel genes ABCTPP, TMSRP1 and TLSRP1 among human gut enterotypes.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 23;8(1):1397. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19862-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29362424 Free PMC article.
-
Review of recent transgenic studies on abiotic stress tolerance and future molecular breeding in potato.Breed Sci. 2015 Mar;65(1):85-102. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.65.85. Epub 2015 Mar 1. Breed Sci. 2015. PMID: 25931983 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E. Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science. 1999;285:1256–1258. - PubMed
-
- Apse MP, Blumwald E. Engineering salt tolerance in plants. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 2002;13:146–150. - PubMed
-
- Baud S, Boutin JP, Miquel M, Lepiniec L, Rochat C. An integrated overview of seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype WS. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 2002;40:151–160.
-
- Bianchi G, Gamba A, Limiroli R, Pozzi N, Elster R, Salamini F, Bartels D. The unusual sugar composition in leaves of the resurrection plant Myrothamnus flabellifolia. Physiologia Plantarum. 1993;87:223–226.
-
- Baroja-Fernández E, Muñoz FJ, Zandueta-Criado A, Morán-Zorzano MT, Viale AM, Alonso-Casajús N, Pozueta-Romero J. Most of the ADP glucose linked to starch biosynthesis occurs outside the chloroplast in source leaves. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA. 2004;101:13080–13085. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

