Insights into substrate stabilization from snapshots of the peptidyl transferase center of the intact 70S ribosome
- PMID: 19363482
- PMCID: PMC2679717
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1577
Insights into substrate stabilization from snapshots of the peptidyl transferase center of the intact 70S ribosome
Abstract
Protein synthesis is catalyzed in the peptidyl transferase center (PTC), located in the large (50S) subunit of the ribosome. No high-resolution structure of the intact ribosome has contained a complete active site including both A- and P-site tRNAs. In addition, although past structures of the 50S subunit have found no ordered proteins at the PTC, biochemical evidence suggests that specific proteins are capable of interacting with the 3' ends of tRNA ligands. Here we present structures, at 3.6-A and 3.5-A resolution respectively, of the 70S ribosome in complex with A- and P-site tRNAs that mimic pre- and post-peptidyl-transfer states. These structures demonstrate that the PTC is very similar between the 50S subunit and the intact ribosome. They also reveal interactions between the ribosomal proteins L16 and L27 and the tRNA substrates, helping to elucidate the role of these proteins in peptidyl transfer.
Figures

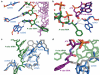
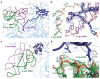
References
-
- Nissen P, Hansen J, Ban N, Moore PB, Steitz TA. The structural basis of ribosome activity in peptide bond synthesis. Science. 2000;289:920–30. - PubMed
-
- Steitz TA. Structural insights into the functions of the large ribosomal subunit, a major antibiotic target. Keio J Med. 2008;57:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Rodnina MV, Beringer M, Wintermeyer W. Mechanism of peptide bond formation on the ribosome. Q Rev Biophys. 2006;39:203–25. - PubMed
-
- Korostelev A, Trakhanov S, Laurberg M, Noller HF. Crystal structure of a 70S ribosome-tRNA complex reveals functional interactions and rearrangements. Cell. 2006;126:1065–77. - PubMed
-
- Bashan A, et al. Structural basis of the ribosomal machinery for peptide bond formation, translocation, and nascent chain progression. Mol Cell. 2003;11:91–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

