A human polymorphism affects NEDD4L subcellular targeting by leading to two isoforms that contain or lack a C2 domain
- PMID: 19364400
- PMCID: PMC2678989
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-10-26
A human polymorphism affects NEDD4L subcellular targeting by leading to two isoforms that contain or lack a C2 domain
Abstract
Background: Ubiquitination serves multiple cellular functions, including proteasomal degradation and the control of stability, function, and intracellular localization of a wide variety of proteins. NEDD4L is a member of the HECT class of E3 ubiquitin ligases. A defining feature of NEDD4L protein isoforms is the presence or absence of an amino-terminal C2 domain, a class of subcellular, calcium-dependent targeting domains. We previously identified a common variant in human NEDD4L that generates isoforms that contain or lack a C2 domain.
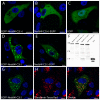
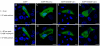
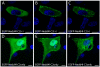
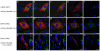
Results: To address the potential functional significance of the NEDD4L common variant on NEDD4L subcellular localization, NEDD4L isoforms that either contained or lacked a C2 domain were tagged with enhanced green fluorescent protein, transfected into Xenopus laevis kidney epithelial cells, and imaged by performing confocal microscopy on live cells. We report that the presence or absence of this C2 domain exerts differential effects on the subcellular distribution of NEDD4L, the ability of C2 containing and lacking NEDD4L isoforms to mobilize in response to a calcium stimulus, and the intracellular transport of subunits of the NEDD4L substrate, ENaC. Furthermore, the ability of the C2-containing isoform to influence beta-ENaC mobilization from intracellular pools involves the NEDD4L active site for ubiquitination. We propose a model to account for the potential impact of this common genetic variant on protein function at the cellular level.
Conclusion: NEDD4L isoforms that contain or lack a C2 domain target different intracellular locations. Additionally, whereas the C2-containing NEDD4L isoform is capable of shuttling between the plasma membrane and intracellular compartments in response to calcium stimulus the C2-lacking isoform can not. The C2-containing isoform differentially affects the mobilization of ENaC subunits from intracellular pools and this trafficking step requires NEDD4L ubiquitin ligase activity. This observation suggests a new mechanism for the requirement for the PY motif in cAMP-mediated exocytosis of ENaC. We have elucidated how a common genetic variant can underlie significant functional diversity in NEDD4L at the cellular level. We propose a model that describes how that functional variation may influence blood pressure. Moreover, our observations regarding differential function of the NEDD4L isoforms may impact other aspects of physiology that involve this ubiquitin ligase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calcium activates Nedd4 E3 ubiquitin ligases by releasing the C2 domain-mediated auto-inhibition.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 16;285(16):12279-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.086405. Epub 2010 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20172859 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 2-45 (Usp2-45) binds to epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC)-ubiquitylating enzyme Nedd4-2.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):F189-96. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00487.2010. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21478478
-
The Nedd4L ubiquitin ligase is activated by FCHO2-generated membrane curvature.EMBO J. 2024 Dec;43(23):5883-5909. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00268-1. Epub 2024 Oct 14. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39402328 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by Nedd4 and ubiquitination.Kidney Int. 2000 Mar;57(3):809-15. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00919.x. Kidney Int. 2000. PMID: 10720933 Review.
-
Physiological Functions of the Ubiquitin Ligases Nedd4-1 and Nedd4-2.Physiology (Bethesda). 2024 Jan 1;39(1):18-29. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00023.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Physiology (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 37962894 Review.
Cited by
-
Epilepsy-associated gene Nedd4-2 mediates neuronal activity and seizure susceptibility through AMPA receptors.PLoS Genet. 2017 Feb 17;13(2):e1006634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006634. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28212375 Free PMC article.
-
The role of WWP1 and WWP2 in bone/cartilage development and diseases.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Nov;479(11):2907-2919. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04917-7. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38252355 Review.
-
The primate-specific Nedd4-1(NE) localizes to late endosomes in response to amino acids to suppress autophagy.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 18;16(1):2682. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57944-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40102426 Free PMC article.
-
Blood pressure and amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in vascular and renal cells.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014 Mar;10(3):146-57. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2013.275. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24419567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism of neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down-regulated 4-2 (Nedd4-2)/NEDD4L-catalyzed polyubiquitin chain assembly.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 24;292(47):19521-19536. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.817882. Epub 2017 Sep 28. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28972136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mukhopadhyay D, Riezman H. Proteasome-independent functions of ubiquitin in endocytosis and signaling. Science. 2007;315:201–205. - PubMed
-
- Ciechanover A, Schwartz AL. The ubiquitin system: pathogenesis of human diseases and drug targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1695:3–17. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Joazeiro CA, Weissman AM. RING finger proteins: mediators of ubiquitin ligase activity. Cell. 2000;102:549–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

