AKAP-scaffolding proteins and regulation of cardiac physiology
- PMID: 19364910
- PMCID: PMC2751630
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00041.2008
AKAP-scaffolding proteins and regulation of cardiac physiology
Abstract
A kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) compose a growing list of diverse but functionally related proteins defined by their ability to bind to the regulatory subunit of protein kinase A. AKAPs perform an integral role in the spatiotemporal modulation of a multitude of cellular signaling pathways. This review highlights the extensive role of AKAPs in cardiac excitation/contraction coupling and cardiac physiology. The literature shows that particular AKAPs are involved in cardiac Ca(2+) influx, release, reuptake, and myocyte repolarization. Studies have also suggested roles for AKAPs in cardiac remodeling. Transgenic studies show functional effects of AKAPs, not only in the cardiovascular system but in other organ systems as well.
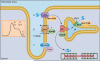
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promotion and inhibition of cardiac hypertrophy by A-kinase anchor proteins.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Sep;90(9):1161-70. doi: 10.1139/y2012-032. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22856508 Review.
-
A-kinase anchoring proteins that regulate cardiac remodeling.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;58(5):451-8. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31821c0220. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22075671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A-kinase anchoring proteins: scaffolding proteins in the heart.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Nov;301(5):H1742-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00569.2011. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21856912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct AKAP-mediated protein-protein interactions as potential drug targets.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008;(186):483-503. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-72843-6_20. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18491065 Review.
-
AKAPs: the architectural underpinnings of local cAMP signaling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Feb;52(2):351-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.05.002. Epub 2011 May 11. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 21600214 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromodomain helicase binding protein 8 (Chd8) is a novel A-kinase anchoring protein expressed during rat cardiac development.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046316. Epub 2012 Oct 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23071553 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of AKAP150 promotes pathological remodelling and heart failure propensity by disrupting calcium cycling and contractile reserve.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Feb;113(2):147-159. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw221. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 27856611 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin 1 enhances neovascularization and reduces ventricular remodeling during chronic myocardial infarction: a study using thioredoxin 1 transgenic mice.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 Jan;50(1):239-47. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.11.002. Epub 2010 Nov 11. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21074540 Free PMC article.
-
CaV1.2 signaling complexes in the heart.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 May;58:143-52. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.12.006. Epub 2012 Dec 22. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23266596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) Tethers EPAC1 in a vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-Cad)-based signaling complex and controls cAMP-mediated vascular permeability.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 29;285(44):33614-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.140004. Epub 2010 Aug 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20732872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altier C, Dubel SJ, Barrere C, Jarvis SE, Stotz SC, Spaetgens RL, Scott JD, Cornet V, De Waard M, Zamponi GW, Nargeot J, Bourinet E. Trafficking of L-type calcium channels mediated by the postsynaptic scaffolding protein AKAP79. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2002;277:33598–33603. - PubMed
-
- Appert-Collin A, Cotecchia S, Nenniger-Tosato M, Pedrazzini T, Diviani D. The A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP)-Lbc-signaling complex mediates alpha1 adrenergic receptor-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104:10140–10145. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellin RM, Sernett SW, Becker B, Ip W, Huiatt TW, Robson RM. Molecular characteristics and interactions of the intermediate filament protein synemin. Interactions with alpha-actinin may anchor synemin-containing heterofilaments. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1999;274:29493–29499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

