A conserved CCCH-type zinc finger protein regulates mRNA nuclear adenylation and export
- PMID: 19364924
- PMCID: PMC2700372
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200811072
A conserved CCCH-type zinc finger protein regulates mRNA nuclear adenylation and export
Abstract
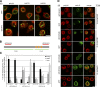
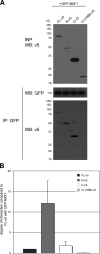
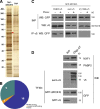
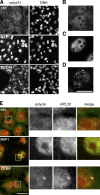
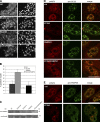
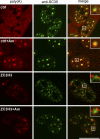
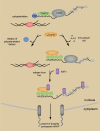
Coupling of messenger RNA (mRNA) nuclear export with prior processing steps aids in the fidelity and efficiency of mRNA transport to the cytoplasm. In this study, we show that the processes of export and polyadenylation are coupled via the Drosophila melanogaster CCCH-type zinc finger protein CG6694/dZC3H3 through both physical and functional interactions. We show that depletion of dZC3H3 from S2R+ cells results in transcript hyperadenylation. Using targeted coimmunoprecipitation and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (MS)/MS techniques, we characterize interactions of known components of the mRNA nuclear export and polyadenylation machineries with dZC3H3. Furthermore, we demonstrate the functional conservation of this factor, as depletion of its human homologue ZC3H3 by small interfering RNA results in an mRNA export defect in human cells as well. Nuclear polyadenylated (poly(A)) RNA in ZC3H3-depleted cells is sequestered in foci removed from SC35-containing speckles, indicating a shift from the normal subnuclear distribution of poly(A) RNA. Our data suggest a model wherein ZC3H3 interfaces between the polyadenylation machinery, newly poly(A) mRNAs, and factors for transcript export.
Figures

References
-
- Benoit B., Mitou G., Chartier A., Temme C., Zaessinger S., Wahle E., Busseau I., Simonelig M. 2005. An essential cytoplasmic function for the nuclear poly(A) binding protein, PABP2, in poly(A) tail length control and early development in Drosophila.Dev. Cell. 9:511–522 - PubMed
-
- Bernardi R., Pandolfi P.P. 2007. Structure, dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies.Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8:1006–1016 - PubMed
-
- Brawerman G. 1981. The role of the poly(A) sequence in mammalian messenger RNA.CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 10:1–38 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

