Neuropilin-1 identifies endothelial precursors in human and murine embryonic stem cells before CD34 expression
- PMID: 19364973
- PMCID: PMC2774135
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.849596
Neuropilin-1 identifies endothelial precursors in human and murine embryonic stem cells before CD34 expression
Abstract
Background: In murine embryonic stem cells, the onset of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) expression identifies endothelial precursors. Undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells express VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-2 expression persists on differentiation. The objective of our study was to identify a single population of endothelial precursors with common identifying features from both human and murine embryonic stem cells.
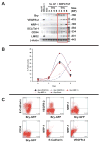
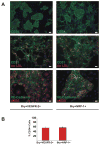
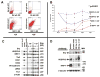
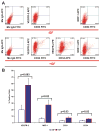
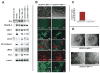
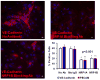
Methods and results: We report that expression of the VEGF coreceptor neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) coincides with expression of Brachyury and VEGFR-2 and identifies endothelial precursors in murine and human embryonic stem cells before CD31 or CD34 expression. When sorted and differentiated, VEGFR-2(+)NRP-1(+) cells form endothelial-like colonies that express CD31 and CD34 7-fold more efficiently than NRP-1 cells. Finally, antagonism of both the VEGF and Semaphorin binding functions of NRP-1 impairs the differentiation of vascular precursors to endothelial cells.
Conclusions: The onset of NRP-1 expression identifies endothelial precursors in murine and human stem cells. The findings define the origin of a single population of endothelial precursors from human and murine stem cells to endothelial cells. Additionally, the function of both the VEGF and Semaphorin binding activities of NRP-1 has important roles in the differentiation of stem cells to endothelial cells, providing novel insights into the role of NRP-1 in a model of vasculogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Drake CJ. Embryonic and adult vasculogenesis. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2003;69:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita J, Itoh H, Hirashima M, Ogawa M, Nishikawa S, Yuruqi T, Naito M, Nakao K, Nishikawa S. Flk1-positive cells derived from embryonic stem cells serve as vascular progenitors. Nature. 2000;408:92–6. - PubMed
-
- Fehling HJ, Lacaud G, Kubo A, Kennedy M, Robertson S, Keller G, Kouskoff V. Tracking mesoderm induction and its specification to the hemangioblast during embryonic stem cell differentiation. Development. 2003;130:4217–27. - PubMed
-
- Sone M, Itoh I, Yamahara K, Yamahara K, Yamashita JK, Yurugi-Kobayashi T, Nonoguchi A, Suzuki Y, Chao T-H, Sawada N, Fukunaga Y, Miyashita K, Park K, Oyamada N, Sawada N, Taura D, Tamura N, Kondo Y, Nito S, Suemori H, Nakatsuji N, Nishikawa S-I, Nakao K. Pathway for differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to vascular cell components and their potential for vascular regeneration. Atheroscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:2127–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

