Epidemiology of incident heart failure in a contemporary elderly cohort: the health, aging, and body composition study
- PMID: 19365001
- PMCID: PMC2756793
- DOI: 10.1001/archinternmed.2009.40
Epidemiology of incident heart failure in a contemporary elderly cohort: the health, aging, and body composition study
Abstract
Background: The race- and sex-specific epidemiology of incident heart failure (HF) among a contemporary elderly cohort are not well described.
Methods: We studied 2934 participants without HF enrolled in the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study (mean [SD] age, 73.6 [2.9] years; 47.9% men; 58.6% white; and 41.4% black) and assessed the incidence of HF, population-attributable risk (PAR) of independent risk factors for HF, and outcomes of incident HF.
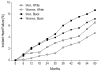
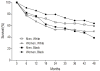
Results: During a median follow-up of 7.1 years, 258 participants (8.8%) developed HF (13.6 cases per 1000 person-years; 95% confidence interval, 12.1-15.4). Men and black participants were more likely to develop HF. No significant sex-based differences were observed in risk factors. Coronary heart disease (PAR, 23.9% for white participants and 29.5% for black participants) and uncontrolled blood pressure (PAR, 21.3% for white participants and 30.1% for black participants) carried the highest PAR in both races. Among black participants, 6 of 8 risk factors assessed (smoking, increased heart rate, coronary heart disease, left ventricular hypertrophy, uncontrolled blood pressure, and reduced glomerular filtration rate) had more than 5% higher PAR compared with that among white participants, leading to a higher overall proportion of HF attributable to modifiable risk factors in black participants vs white participants (67.8% vs 48.9%). Participants who developed HF had higher annual mortality (18.0% vs 2.7%). No racial difference in survival after HF was noted; however, rehospitalization rates were higher among black participants (62.1 vs 30.3 hospitalizations per 100 person-years, P < .001).
Conclusions: Incident HF is common in older persons; a large proportion of HF risk is attributed to modifiable risk factors. Racial differences in risk factors for HF and in hospitalization rates after HF need to be considered in prevention and treatment efforts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Serum Erythropoietin With Cardiovascular Events, Kidney Function Decline, and Mortality: The Health Aging and Body Composition Study.Circ Heart Fail. 2016 Jan;9(1):e002124. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002124. Circ Heart Fail. 2016. PMID: 26721912 Free PMC article.
-
Incident heart failure in relation to vascular disease: insights from the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study.Eur J Heart Fail. 2014 May;16(5):526-34. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.69. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014. PMID: 24578142 Free PMC article.
-
Incident heart failure hospitalization and subsequent mortality in chronic heart failure: a propensity-matched study.J Card Fail. 2008 Apr;14(3):211-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2007.12.001. J Card Fail. 2008. PMID: 18381184 Free PMC article.
-
Risk for Incident Heart Failure: A Subject-Level Meta-Analysis From the Heart "OMics" in AGEing (HOMAGE) Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 May 2;6(5):e005231. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005231. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28465299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidence and epidemiology of heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2000 Jun;5(2):167-73. doi: 10.1023/A:1009884820941. Heart Fail Rev. 2000. PMID: 16228142 Review.
Cited by
-
Administration of cardiac stem cells in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: the SCIPIO trial: surgical aspects and interim analysis of myocardial function and viability by magnetic resonance.Circulation. 2012 Sep 11;126(11 Suppl 1):S54-64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.092627. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 22965994 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Resting heart rate and risk of incident heart failure: three prospective cohort studies and a systematic meta-analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2015 Jan 14;4(1):e001364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001364. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015. PMID: 25589535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heart Failure Epidemiology and Outcomes Statistics: A Report of the Heart Failure Society of America.J Card Fail. 2023 Oct;29(10):1412-1451. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2023.07.006. Epub 2023 Sep 26. J Card Fail. 2023. PMID: 37797885 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Role of Hypertension in Race-Ethnic Disparities in Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep. 2015 Apr;9(4):18. doi: 10.1007/s12170-015-0446-5. Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep. 2015. PMID: 26401192 Free PMC article.
-
Racial differences in incident heart failure among young adults.N Engl J Med. 2009 Mar 19;360(12):1179-90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0807265. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19297571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2007 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115(5):e69–171. - PubMed
-
- Ammar KA, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW, et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of heart failure stages: application of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association heart failure staging criteria in the community. Circulation. 2007;115(12):1563–1570. - PubMed
-
- Bleumink GS, Knetsch AM, Sturkenboom MC, et al. Quantifying the heart failure epidemic: prevalence, incidence rate, lifetime risk and prognosis of heart failure The Rotterdam Study. Eur Heart J. 2004;25(18):1614–1619. - PubMed
-
- Levy D, Kenchaiah S, Larson MG, et al. Long-term trends in the incidence of and survival with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(18):1397–1402. - PubMed
-
- Roger VL, Weston SA, Redfield MM, et al. Trends in heart failure incidence and survival in a community-based population. JAMA. 2004;292(3):344–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

