Remarkable resilience of teeth
- PMID: 19365079
- PMCID: PMC2678632
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0902466106
Remarkable resilience of teeth
Abstract
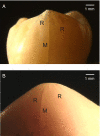
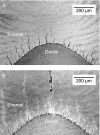
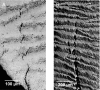
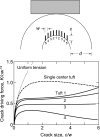
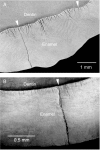
Tooth enamel is inherently weak, with fracture toughness comparable with glass, yet it is remarkably resilient, surviving millions of functional contacts over a lifetime. We propose a microstructural mechanism of damage resistance, based on observations from ex situ loading of human and sea otter molars (teeth with strikingly similar structural features). Section views of the enamel implicate tufts, hypomineralized crack-like defects at the enamel-dentin junction, as primary fracture sources. We report a stabilization in the evolution of these defects, by "stress shielding" from neighbors, by inhibition of ensuing crack extension from prism interweaving (decussation), and by self-healing. These factors, coupled with the capacity of the tooth configuration to limit the generation of tensile stresses in largely compressive biting, explain how teeth may absorb considerable damage over time without catastrophic failure, an outcome with strong implications concerning the adaptation of animal species to diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lucas PW, Peters CR, Arrandale S. Seed-breaking forces exerted by orangutans with their teeth in captivity and a new technique for estimating forces produced in the wild. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1994;9:365–378. - PubMed
-
- Braun S, et al. A study of bite force. 1. Relationship to various physical characteristics. Angle Orthodontist. 1995;65:367–372. - PubMed
-
- Kamat S, Su X, Ballarini R, Heuer AH. Structural basis for the fracture toughness of the shell of the conch Strombus gigas. Nature. 2000;405:1036–1040. - PubMed
-
- Evans AG, et al. Model for the robust mechanical behavior of nacre. J Mater Res. 2001;16:2475–2484.
-
- Rasmussen ST, Patchin RE, Scott DB, Heuer AH. Fracture properties of human enamel and dentin. J Dent Res. 1976;55:154–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

