IL-10 is up-regulated in multiple cell types during viremic HIV infection and reversibly inhibits virus-specific T cells
- PMID: 19365081
- PMCID: PMC2714209
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-12-191296
IL-10 is up-regulated in multiple cell types during viremic HIV infection and reversibly inhibits virus-specific T cells
Abstract
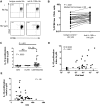
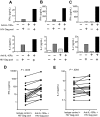
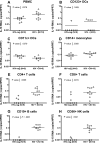
Murine models indicate that interleukin-10 (IL-10) can suppress viral clearance, and interventional blockade of IL-10 activity has been proposed to enhance immunity in chronic viral infections. Increased IL-10 levels have been observed during HIV infection and IL-10 blockade has been shown to enhance T-cell function in some HIV-infected subjects. However, the categories of individuals in whom the IL-10 pathway is up-regulated are poorly defined, and the cellular sources of IL-10 in these subjects remain to be determined. Here we report that blockade of the IL-10 pathway augmented in vitro proliferative capacity of HIV-specific CD4 and CD8 T cells in individuals with ongoing viral replication. IL-10 blockade also increased cytokine secretion by HIV-specific CD4 T cells. Spontaneous IL-10 expression, measured as either plasma IL-10 protein or IL-10 mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), correlated positively with viral load and diminished after successful antiretroviral therapy. IL-10 mRNA levels were up-regulated in multiple PBMC subsets in HIV-infected subjects compared with HIV-negative controls, particularly in T, B, and natural killer (NK) cells, whereas monocytes were a major source of IL-10 mRNA in HIV-infected and -uninfected individuals. These data indicate that multiple cell types contribute to IL-10-mediated immune suppression in the presence of uncontrolled HIV viremia.
Figures




Comment in
-
Suppressing the suppressor.Blood. 2009 Jul 9;114(2):233. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-218073. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19589930 No abstract available.
References
-
- Munier ML, Kelleher AD. Acutely dysregulated, chronically disabled by the enemy within: T-cell responses to HIV-1 infection. Immunol Cell Biol. 2007;85:6–15. - PubMed
-
- Shin H, Wherry EJ. CD8 T cell dysfunction during chronic viral infection. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:408–415. - PubMed
-
- Chougnet C, Gessani S. Role of gp120 in dendritic cell dysfunction in HIV infection. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;80:994–1000. - PubMed
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, et al. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439:682–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

