Ketohexokinase: expression and localization of the principal fructose-metabolizing enzyme
- PMID: 19365088
- PMCID: PMC2713076
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2009.953190
Ketohexokinase: expression and localization of the principal fructose-metabolizing enzyme
Abstract
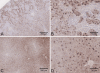
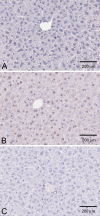
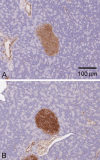
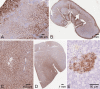
Ketohexokinase (KHK, also known as fructokinase) initiates the pathway through which most dietary fructose is metabolized. Very little is known about the cellular localization of this enzyme. Alternatively spliced KHK-C and KHK-A mRNAs are known, but the existence of the KHK-A protein isoform has not been demonstrated in vivo. Using antibodies to KHK for immunohistochemistry and Western blotting of rodent tissues, including those from mouse knockouts, coupled with RT-PCR assays, we determined the distribution of the splice variants. The highly expressed KHK-C isoform localized to hepatocytes in the liver and to the straight segment of the proximal renal tubule. In both tissues, cytoplasmic and nuclear staining was observed. The KHK-A mRNA isoform was observed exclusively in a range of other tissues, and by Western blotting, the presence of endogenous immunoreactive KHK-A protein was shown for the first time, proving that the KHK-A mRNA is translated into KHK-A protein in vivo, and supporting the suggestion that this evolutionarily conserved isoform is physiologically functional. However, the low levels of KHK-A expression prevented its immunohistochemical localization within these tissues. Our results highlight that the use of in vivo biological controls (tissues from knockout animals) is required to distinguish genuine KHK immunoreactivity from experimental artifact.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIF-driven SF3B1 induces KHK-C to enforce fructolysis and heart disease.Nature. 2015 Jun 25;522(7557):444-449. doi: 10.1038/nature14508. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26083752 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue expression of ketohexokinase in cats.Res Vet Sci. 2009 Aug;87(1):115-7. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2008.11.004. Epub 2008 Dec 23. Res Vet Sci. 2009. PMID: 19108855
-
Both isoforms of ketohexokinase are dispensable for normal growth and development.Physiol Genomics. 2010 Nov 29;42A(4):235-43. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00128.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Physiol Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20841500
-
Fructose and fructose kinase in cancer and other pathologies.J Genet Genomics. 2021 Jul 20;48(7):531-539. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.06.006. Epub 2021 Jul 7. J Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34326012 Review.
-
Fructose metabolism, cardiometabolic risk, and the epidemic of coronary artery disease.Eur Heart J. 2018 Jul 7;39(26):2497-2505. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx518. Eur Heart J. 2018. PMID: 29020416 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of long-term dehydration and quick rehydration on the camel kidney: pathological changes and modulation of the expression of solute carrier proteins and aquaporins.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Aug 16;20(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04215-4. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39148099 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactivity-Guided Identification of Botanical Inhibitors of Ketohexokinase.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 20;11(6):e0157458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157458. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27322374 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of dietary fructose on gut permeability, microbiota, abdominal adiposity, insulin signaling and reproductive function.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 9;9(8):e18896. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18896. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37636431 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacophore-based virtual screening and in silico investigations of small molecule library for discovery of human hepatic ketohexokinase inhibitors for the treatment of fructose metabolic disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 7;16:1531512. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1531512. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40260383 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in renal and metabolic responses to a high-fructose diet in mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Mar 1;308(5):F400-10. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00403.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25537743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelman RC, Ballard FJ, Weinhouse S (1967) Purification and properties of rat liver fructokinase. J Biol Chem 242:3360–3365 - PubMed
-
- Asipu A, Hayward BE, O’Reilly J, Bonthron DT (2003) Properties of normal and mutant recombinant human ketohexokinases and implications for the pathogenesis of essential fructosuria. Diabetes 52:2426–2432 - PubMed
-
- Barski OA, Papusha VZ, Ivanova MM, Rudman DM, Finegold MJ (2005) Developmental expression and function of aldehyde reductase in proximal tubules of the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F200–207 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

