Endocrine cell clustering during human pancreas development
- PMID: 19365093
- PMCID: PMC2728126
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2009.953307
Endocrine cell clustering during human pancreas development
Abstract
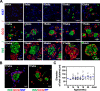
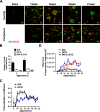
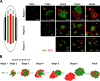
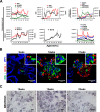
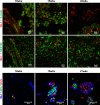
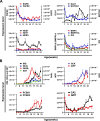
The development of efficient, reproducible protocols for directed in vitro differentiation of human embryonic stem (hES) cells into insulin-producing beta cells will benefit greatly from increased knowledge regarding the spatiotemporal expression profile of key instructive factors involved in human endocrine cell generation. Human fetal pancreases 7 to 21 weeks of gestational age, were collected following consent immediately after pregnancy termination and processed for immunostaining, in situ hybridization, and real-time RT-PCR expression analyses. Islet-like structures appear from approximately week 12 and, unlike the mixed architecture observed in adult islets, fetal islets are initially formed predominantly by aggregated insulin- or glucagon-expressing cells. The period studied (7-22 weeks) coincides with a decrease in the proliferation and an increase in the differentiation of the progenitor cells, the initiation of NGN3 expression, and the appearance of differentiated endocrine cells. The present study provides a detailed characterization of islet formation and expression profiles of key intrinsic and extrinsic factors during human pancreas development. This information is beneficial for the development of efficient protocols that will allow guided in vitro differentiation of hES cells into insulin-producing cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rfx6 is an Ngn3-dependent winged helix transcription factor required for pancreatic islet cell development.Development. 2010 Jan;137(2):203-12. doi: 10.1242/dev.041673. Development. 2010. PMID: 20040487 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA miR-7 is preferentially expressed in endocrine cells of the developing and adult human pancreas.Gene Expr Patterns. 2009 Apr;9(4):193-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2008.12.003. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Gene Expr Patterns. 2009. PMID: 19135553
-
Imaging Human Pancreatic Endocrinogenesis During Early Prenatal Life.Diabetes. 2025 Mar 1;74(3):368-375. doi: 10.2337/db24-0641. Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 39602451 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of pancreatic islet cells from human embryonic stem cells.Sci China C Life Sci. 2009 Jul;52(7):615-21. doi: 10.1007/s11427-009-0095-3. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Sci China C Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19641866 Review.
-
Conversion of embryonic stem cells into pancreatic beta-cell surrogates guided by ontogeny.Regen Med. 2006 May;1(3):327-36. doi: 10.2217/17460751.1.3.327. Regen Med. 2006. PMID: 17465786 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional, metabolic and transcriptional maturation of human pancreatic islets derived from stem cells.Nat Biotechnol. 2022 Jul;40(7):1042-1055. doi: 10.1038/s41587-022-01219-z. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Nat Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35241836 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical characterisation of cells co-producing insulin and glucagon in the developing human pancreas.Diabetologia. 2012 Feb;55(2):372-81. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2344-9. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22038519
-
Endogenous Pancreatic β Cell Regeneration: A Potential Strategy for the Recovery of β Cell Deficiency in Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Feb 20;10:101. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00101. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30842756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of Insulin in Insulin-Deficient Islets of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 19;15(1):125. doi: 10.3390/life15010125. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860066 Free PMC article.
-
A 3D system to model human pancreas development and its reference single-cell transcriptome atlas identify signaling pathways required for progenitor expansion.Nat Commun. 2021 May 25;12(1):3144. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23295-6. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34035279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlgren U, Pfaff SL, Jessell TM, Edlund T, Edlund H (1997) Independent requirement for ISL1 in formation of pancreatic mesenchyme and islet cells. Nature 385:257–260 - PubMed
-
- Apelqvist A, Li H, Sommer L, Beatus P, Anderson DJ, Honjo T, Hrabe de Angelis M, et al. (1999) Notch signalling controls pancreatic cell differentiation. Nature 400:877–881 - PubMed
-
- Bhushan A, Itoh N, Kato S, Thiery JP, Czernichow P, Bellusci S, Scharfmann R (2001) Fgf10 is essential for maintaining the proliferative capacity of epithelial progenitor cells during early pancreatic organogenesis. Development 128:5109–5117 - PubMed
-
- Bocian-Sobkowska J, Zabel M, Wozniak W, Surdyk-Zasada J (1999) Polyhormonal aspect of the endocrine cells of the human fetal pancreas. Histochem Cell Biol 112:147–153 - PubMed
-
- Bonal C, Herrera PL (2008) Genes controlling pancreas ontogeny. Int J Dev Biol 52:823–835 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

