Microfluidic cell counter with embedded optical fibers fabricated by femtosecond laser ablation and anodic bonding
- PMID: 19365429
- PMCID: PMC3155247
- DOI: 10.1364/oe.17.006068
Microfluidic cell counter with embedded optical fibers fabricated by femtosecond laser ablation and anodic bonding
Abstract
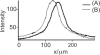
A simple fabrication technique to create all silicon/glass microfluidic devices is demonstrated using femtosecond laser ablation and anodic bonding. In a first application, we constructed a cell counting device based on small angle light scattering. The counter featured embedded optical fibers for multiangle excitation and detection of scattered light and/or fluorescence. The performance of the microfluidic cell counter was benchmarked against a commercial fluorescence-activated cell sorter.
Figures


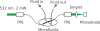
References
-
- Altendorf E, Zebert D, Holl M, Yager P. Differential blood cell counts obtained using a microchannel based flow cytometer. IEEE International Conference on Solid-State Sensors and Actuators; IEEE; 1997. pp. 531–534.
-
- Brown M, Wittwer C. Flow cytometry: principles and clinical applications in hematology. Clin. Chem. 2000;46:1221–1229. - PubMed
-
- Pamme N, Koyama R, Manz A. Counting and sizing of particles and particle agglomerates in a microfluidic device using laser light scattering: application to a particle-enhanced immunoassay. Lab Chip. 2003;3:187–192. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Wang Y. Optical microflow cytometer for particle counting, sizing and fluorescence detection. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2008 DOI 10.1007/s10404-008-0335-z.
-
- Chabinyc ML, Chiu DT, Cooper McDonald J, Stroock AD, Christian JF, Karger AM, Whitesides GM. An integrated fluorescence detection system in poly(dimethylsiloxane) for microfluidic applications. Anal. Chem. 2001;73:4491–4498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

