Smoothened adopts multiple active and inactive conformations capable of trafficking to the primary cilium
- PMID: 19365551
- PMCID: PMC2664476
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005182
Smoothened adopts multiple active and inactive conformations capable of trafficking to the primary cilium
Abstract
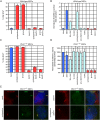
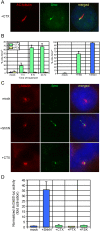
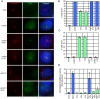
Activation of Hedgehog (Hh) signaling requires the transmembrane protein Smoothened (Smo), a member of the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily. In mammals, Smo translocates to the primary cilium upon binding of Hh ligands to their receptor, Patched (Ptch1), but it is unclear if ciliary trafficking of Smo is sufficient for pathway activation. Here, we demonstrate that cyclopamine and jervine, two structurally related inhibitors of Smo, force ciliary translocation of Smo. Treatment with SANT-1, an unrelated Smo antagonist, abrogates cyclopamine- and jervine-mediated Smo translocation. Further, activation of protein kinase A, either directly or through activation of Galphas, causes Smo to translocate to a proximal region of the primary cilium. We propose that Smo adopts multiple inactive and active conformations, which influence its localization and trafficking on the primary cilium.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hedgehog-stimulated chemotaxis is mediated by smoothened located outside the primary cilium.Sci Signal. 2012 Aug 21;5(238):ra60. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002798. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22912493 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ciliary trafficking in Hedgehog receptor signaling.Sci Signal. 2015 Jun 2;8(379):ra55. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa5622. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 26038600 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule imaging of Hedgehog pathway protein Smoothened in primary cilia reveals binding events regulated by Patched1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 7;112(27):8320-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1510094112. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26100903 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic Hedgehog activates the GTPases Rac1 and RhoA in a Gli-independent manner through coupling of smoothened to Gi proteins.Sci Signal. 2011 Nov 22;4(200):pt7. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002396. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 22114142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog signaling pathway: a novel model and molecular mechanisms of signal transduction.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Apr;73(7):1317-32. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2127-4. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26762301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hedgehog-stimulated chemotaxis is mediated by smoothened located outside the primary cilium.Sci Signal. 2012 Aug 21;5(238):ra60. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002798. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22912493 Free PMC article.
-
Gli2 trafficking links Hedgehog-dependent activation of Smoothened in the primary cilium to transcriptional activation in the nucleus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Dec 22;106(51):21666-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912180106. Epub 2009 Dec 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19996169 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Smoothened inhibitor, IPI-926, on smoothened ciliary localization and Hedgehog pathway activity.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 7;9(3):e90534. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090534. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24608250 Free PMC article.
-
NL-103, a novel dual-targeted inhibitor of histone deacetylases and hedgehog pathway, effectively overcomes vismodegib resistance conferred by Smo mutations.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2014 Jun;2(3):e00043. doi: 10.1002/prp2.43. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2014. PMID: 25505589 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic Hedgehog dependent phosphorylation by CK1α and GRK2 is required for ciliary accumulation and activation of smoothened.PLoS Biol. 2011 Jun;9(6):e1001083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001083. Epub 2011 Jun 14. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21695114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McMahon AP, Ingham PW, Tabin CJ. Developmental roles and clinical significance of hedgehog signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2003;53:1–114. - PubMed
-
- Taipale J, Cooper MK, Maiti T, Beachy PA. Patched acts catalytically to suppress the activity of Smoothened. Nature. 2002;418:892–897. - PubMed
-
- Huangfu D, Anderson KV. Signaling from Smo to Ci/Gli: conservation and divergence of Hedgehog pathways from Drosophila to vertebrates. Development. 2006;133:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Varjosalo M, Li SP, Taipale J. Divergence of hedgehog signal transduction mechanism between Drosophila and mammals. Dev Cell. 2006;10:177–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

