Characterization of persistent TTX-R Na+ currents in physiological concentration of sodium in rat visceral afferents
- PMID: 19365577
- PMCID: PMC2667275
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.5.293
Characterization of persistent TTX-R Na+ currents in physiological concentration of sodium in rat visceral afferents
Abstract
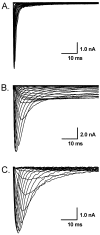
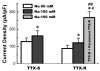
Persistent tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-R) Na(+) (Na(v)1.9/SCN11A) currents are not normally recorded in vagal afferent neurons (VANs) with 50 mM of extracellular Na(+) although the functional expression of this current was observed in the presence of PGE(2) or forskolin. However, it is uncertain whether this current can be seen under physiological condition (150 mM Na(+)). Using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique, we showed that persistent TTX-R Na(+) currents were expressed in 9 out of 38 VANs bathed in 150 mM Na(+). The current density, but not the whole-cell capacitance, was significantly enhanced in the VANs expressing Nav1.9. Persistent TTX-R Na(+) channels were activated at a more hyperpolarized membrane potential near -60 mV, compared with TTX-sensitive (TTX-S at -40 mV) and TTX-R Na(+) channels (at -20 mV). This indicates that persistent TTX-R Na(+) channels provide a wider activation window than TTX-S and TTX-R Na channels to up-regulate neuronal excitability. These results suggest that the persistent TTX-R Na(+) currents may be involved in the neuronal excitability by setting a lower pressure-discharge threshold and higher discharge frequency of VANs, especially the unique subset and gender-specific distribution of myelinated Ah-type VANs, including Ah-type aortic baroreceptor neurons, identified in our previous study.
Keywords: Ion channel; Patch technique; Sodium; Tetrodotoxin; Visceral afferent.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E2-mediated upregulation of neuroexcitation and persistent tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) currents in Ah-type trigeminal ganglion neurons isolated from adult female rats.Neuroscience. 2016 Apr 21;320:194-204. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.008. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26868972
-
Analysis of the variation in use-dependent inactivation of high-threshold tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium currents recorded from rat sensory neurons.Neuroscience. 2006 Dec 28;143(4):923-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.052. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 17027172
-
Propranolol modulation of tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channels in dural afferent neurons.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 5;910:174449. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174449. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34454925
-
Tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ currents and inflammatory hyperalgesia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jul 6;96(14):7645-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.14.7645. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10393874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1994 Jun;14(3):227-44. doi: 10.1007/BF02088322. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1994. PMID: 7712513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The venom of the spider Selenocosmia jiafu contains various neurotoxins acting on voltage-gated ion channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Mar 5;6(3):988-1001. doi: 10.3390/toxins6030988. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24603666 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine-mediated afferent-specific presynaptic transmission blocks in low-threshold and sex-specific subpopulation of myelinated Ah-type baroreceptor neurons of rats.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44108-22. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6586. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26675761 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological properties of embryonic stem cell-derived neurons.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024169. Epub 2011 Aug 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887381 Free PMC article.
-
Caution for Multidrug Therapy: Significant Baroreflex Afferent Neuroexcitation Coordinated by Multi-Channels/Pumps Under the Threshold Concentration of Yoda1 and Dobutamine Combination.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 16;14(10):1311. doi: 10.3390/biom14101311. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456244 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-dependent depressor response of melatonin via baroreflex afferent function and intensification of PKC-mediated Nav1.9 activation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Sep;43(9):2313-2324. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-00867-w. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35132193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li B, Schild JH. Persistent tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ currents are activated by prostaglandin E2 via cyclic AMP-dependent pathway in C-type nodose neurons of adult rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;355:1064–1068. - PubMed
-
- Qiao G, Li S, Yang B et al. Inhibitory effects of artemisinin on voltage-gated ion channels in intact nodose ganglion neurons of adult rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;100:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Qiao GF, Cheng ZF, Huo R et al. GM1 ganglioside contributes to retain the neuronal conduction and neuronal excitability in visceral and baroreceptor afferents. J Neurochem. 2008;106:1637–1645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

