The application of on-chip optofluidic microscopy for imaging Giardia lamblia trophozoites and cysts
- PMID: 19365730
- PMCID: PMC2888668
- DOI: 10.1007/s10544-009-9312-x
The application of on-chip optofluidic microscopy for imaging Giardia lamblia trophozoites and cysts
Abstract
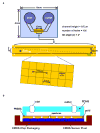
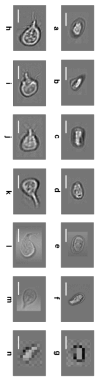
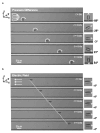
The optofluidic microscope (OFM) is a lensless, low-cost and highly compact on-chip device that can enable high-resolution microscopy imaging. The OFM performs imaging by flowing/scanning the target objects across a slanted hole array; by measuring the time-varying light transmission changes through the holes, we can then render images of the target objects at a resolution that is comparable to the holes' size. This paper reports the adaptation of the OFM for imaging Giardia lamblia trophozoites and cysts, a disease-causing parasite species that is commonly found in poor-quality water sources. We also describe our study of the impact of pressure-based flow and DC electrokinetic-based flow in controlling the flow motion of Giardia cysts--rotation-free translation of the parasite is important for good OFM image acquisition. Finally, we report the successful microscopy imaging of both Giardia trophozoites and cysts with an OFM that has a focal plane resolution of 0.8 microns.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lensless high-resolution on-chip optofluidic microscopes for Caenorhabditis elegans and cell imaging.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Aug 5;105(31):10670-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804612105. Epub 2008 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18663227 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of a color-capable optofluidic microscope on a RGB CMOS color sensor chip substrate.Lab Chip. 2010 Feb 21;10(4):411-4. doi: 10.1039/b919004j. Epub 2010 Jan 5. Lab Chip. 2010. PMID: 20126679 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse macrophages capture and kill Giardia lamblia by means of releasing extracellular trap.Dev Comp Immunol. 2018 Nov;88:206-212. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2018.07.024. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Dev Comp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30048699
-
Imaging and analysis of the microtubule cytoskeleton in giardia.Methods Cell Biol. 2010;97:307-39. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(10)97017-9. Methods Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20719278 Review.
-
The proteasome of the differently-diverged eukaryote Giardia lamblia and its role in remodeling of the microtubule-based cytoskeleton.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2017 Aug;43(4):481-492. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2016.1262814. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28033730 Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging and identification of waterborne parasites using a chip-scale microscope.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 26;9(2):e89712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089712. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586978 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of waterborne parasites using field-portable and cost-effective lensfree microscopy.Lab Chip. 2010 Sep 21;10(18):2419-23. doi: 10.1039/c004829a. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Lab Chip. 2010. PMID: 20694255 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Fabrication of a BiCMOS Dielectric Sensor for Viscosity Measurements: A Possible Solution for Early Detection of COPD.Biosensors (Basel). 2018 Aug 21;8(3):78. doi: 10.3390/bios8030078. Biosensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30134577 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in optical detection technologies in lab-on-a-chip devices for biosensing applications.Sensors (Basel). 2014 Aug 21;14(8):15458-79. doi: 10.3390/s140815458. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25196161 Free PMC article.
-
Optofluidic Technology for Water Quality Monitoring.Micromachines (Basel). 2018 Apr 1;9(4):158. doi: 10.3390/mi9040158. Micromachines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30424092 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chin CD, Linder V, Sia SK. Lab-on-a-chip devices for global health: Past studies and future opportunities. Lab Chip. 2007;7:41–57. - PubMed
-
- Erlandsen SL, Meyer EA. Giardia and Giardiasis: Biology, Pathogenesis, and Epidemiology. Springer; 1984.
-
- Heng X, Erickson D, Baugh LR, Yaqoob Z, Sternberg PW, Psaltis D, Yang C. Optofluidic microscopy- a method for implementing a high resolution optical microscope on a chip. Lab Chip. 2006a;6:1274–1276. - PubMed
-
- Heng X, Cui X, Knapp D, Wu J, Yaqoob Z, McDowell EJ, Psaltis D, Yang C. Determining the resolution limit of nano aperture based optical imaging or sensing device. Optics Express. 2006b;14:10410–10425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

