Regulatory autophosphorylation sites on protein kinase C-delta at threonine-141 and threonine-295
- PMID: 19366211
- PMCID: PMC2737367
- DOI: 10.1021/bi802171c
Regulatory autophosphorylation sites on protein kinase C-delta at threonine-141 and threonine-295
Abstract
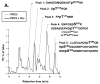
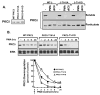
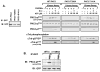
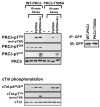
Protein kinase C-delta (PKCdelta) is a Ser/Thr kinase that regulates a wide range of cellular responses. This study identifies novel in vitro PKCdelta autophosphorylation sites at Thr(141) adjacent to the pseudosubstrate domain, Thr(218) in the C1A-C1B interdomain, Ser(295), Ser(302), and Ser(304) in the hinge region, and Ser(503) adjacent to Thr(505) in the activation loop. Cell-based studies show that Thr(141) and Thr(295) also are phosphorylated in vivo and that Thr(141) phosphorylation regulates the kinetics of PKCdelta downregulation in COS7 cells. In vitro studies implicate Thr(141) and Thr(295) autophosphorylation as modifications that regulate PKCdelta activity. A T141D substitution markedly increases basal lipid-independent PKCdelta activity; the PKCdelta-T141D mutant is only slightly further stimulated in vitro by PMA treatment, suggesting that Thr(141) phosphorylation relieves autoinhibitory constraints that limit PKCdelta activity. Mutagenesis studies also indicate that a phosphorylation at Thr(295) contributes to the control of PKCdelta substrate specificity. We previously demonstrated that PKCdelta phosphorylates the myofilament protein cardiac troponin I (cTnI) at Ser(23)/Ser(24) when it is allosterically activated by lipid cofactors and that the Thr(505)/Tyr(311)-phosphorylated form of PKCdelta (that is present in assays with Src) acquires as additional activity toward cTnI-Thr(144). Studies reported herein show that a T505A substitution reduces PKCdelta-Thr(295) autophosphorylation and that a T295A substitution leads to a defect in Src-dependent PKCdelta-Tyr(311) phosphorylation and PKCdelta-dependent cTnI-Thr(144) phosphorylation. These results implicate PKCdelta-Thr(295) autophosphorylation as a lipid-dependent modification that links PKCdelta-Thr(505) phosphorylation to Src-dependent regulation of PKCdelta catalytic function. Collectively, these studies identify novel regulatory autophosphorylations on PKCdelta that serve as markers and regulators of PKCdelta activity.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

