Ileocecal valve lipoma with refractory hemorrhage
- PMID: 19366548
- PMCID: PMC3015905
Ileocecal valve lipoma with refractory hemorrhage
Abstract
Background: Lipomas are the most common benign mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, with the colon being the most prevalent site. Intestinal lipomas are usually asymptomatic. Tumors >2 cm in diameter may occasionally cause nonspecific symptoms, including change in bowel habits, abdominal pain, or rectal bleeding, but with resection the prognosis is excellent. Herein, we describe the case of an elderly male who presented with painless hematochezia.
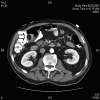
Methods: Both colonoscopy and computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis confirmed the presence of a mass near the ileocecal valve. Because of continuing bleeding, the patient required laparoscopic-assisted right hemicolectomy to resect the mass.
Results: Both gross and microscopic pathology were consistent with lipoma at the ileocecal valve.
Conclusion: Previous cases of ileocecal valve lipomas have been reported in the English literature, with the majority presenting as intussusception or volvulus. We present a rare case of an ulcerated ileocecal valve lipoma presenting as lower gastrointestinal bleeding that was treated successfully with laparoscopic resection.
Figures


References
-
- Katsinelos P, Paroutoglou G, Jouvaras G, et al. Lipohyperplasia of the ileocecal valve as a cause of intussusception. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2005;68:280–282 - PubMed
-
- Meshikhes AW, Al-Momen SA, Al Talaq FT, Al-Jaroof AH. Adult intussusception caused by a lipoma in the small bowel: report of a case. Surg Today. 2005;35:161–165 - PubMed
-
- Parmar JH, Lawrence R, Ridley NT. Submucous lipoma of the ileocaecal valve presenting as caecal volvulus. Int J Clin Pract. 2004;58:424–425 - PubMed
-
- Katsinelos P, Chatzimavroudis G, Zavos C, Paroutoglou G, Papaziogas B, Kountouras J. A novel technique for the treatment of a symptomatic giant colonic lipoma. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2007;17:467–469 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
