Molecular and functional analyses of amino acid decarboxylases involved in cuticle tanning in Tribolium castaneum
- PMID: 19366687
- PMCID: PMC2713571
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M901629200
Molecular and functional analyses of amino acid decarboxylases involved in cuticle tanning in Tribolium castaneum
Abstract
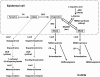
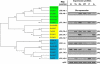
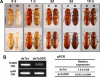
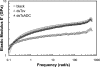
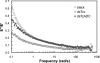
Aspartate 1-decarboxylase (ADC) and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine decarboxylase (DDC) provide beta-alanine and dopamine used in insect cuticle tanning. beta-Alanine is conjugated with dopamine to yield N-beta-alanyldopamine (NBAD), a substrate for the phenol oxidase laccase that catalyzes the synthesis of cuticle protein cross-linking agents and pigment precursors. We identified ADC and DDC genes in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum (Tc), and investigated their functions. TcADC mRNA was most abundant prior to the pupal-adult molt. Injection of TcADC double-stranded (ds) RNA (dsTcADC) into mature larvae resulted in depletion of NBAD in pharate adults, accumulation of dopamine, and abnormally dark pigmentation of the adult cuticle. Injection of beta-alanine, the expected product of ADC, into dsTcADC-treated pupae rescued the pigmentation phenotype, resulting in normal rust-red color. A similar pattern of catechol content consisting of elevated dopamine and depressed NBAD was observed in the genetic black mutants of Tribolium, in which levels of TcADC mRNA were drastically reduced. Furthermore, from the Tribolium black mutant and dsTcADC-injected insects both exhibited similar changes in material properties. Dynamic mechanical analysis of elytral cuticle from beetles with depleted TcADC transcripts revealed diminished cross-linking of cuticular components, further confirming the important role of oxidation products of NBAD as cross-linking agents during cuticle tanning. Injection of dsTcDDC into larvae produced a lethal pupal phenotype, and the resulting grayish pupal cuticle exhibited many small patches of black pigmentation. When dsTcDDC was injected into young pupae, the resulting adults had abnormally dark brown body color, but there was little mortality. Injection of dsTcDDC resulted in more than a 5-fold increase in levels of DOPA, indicating that lack of TcDDC led to accumulation of its substrate, DOPA.
Figures



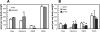


References
-
- Andersen S. C. ( 2005) in Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science ( Gilbert L. I., Iatrou K., Gills S. eds) Vol. 4, pp. 145– 170, Elsevier Press, Oxford, UK
-
- Hopkins T. L., Kramer K. J. ( 1992) Annu. Rev. Entomol. 37, 273– 302
-
- Kramer K. J., Kanost M. R., Hopkins T. L., Jiang H., Zhu Y. C., Xu R., Kerwin J. L., Turecek F. ( 2001) Tetrahedron 57, 385– 392
-
- Hopkins T. L., Morgan T. D., Kramer K. J. ( 1984) Insect Biochem. 14, 533– 540
-
- Morgan T. D., Hopkins T. L., Kramer K. J., Roseland C. R., Czapla T. H., Tomer K. B., Crow F. W. ( 1987) Insect Biochem. 17, 255– 263
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

