Computationally guided photothermal tumor therapy using long-circulating gold nanorod antennas
- PMID: 19366797
- PMCID: PMC2712876
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4242
Computationally guided photothermal tumor therapy using long-circulating gold nanorod antennas
Abstract
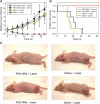
Plasmonic nanomaterials have the opportunity to considerably improve the specificity of cancer ablation by i.v. homing to tumors and acting as antennas for accepting externally applied energy. Here, we describe an integrated approach to improved plasmonic therapy composed of multimodal nanomaterial optimization and computational irradiation protocol development. We synthesized polyethylene glycol (PEG)-protected gold nanorods (NR) that exhibit superior spectral bandwidth, photothermal heat generation per gram of gold, and circulation half-life in vivo (t(1/2), approximately 17 hours) compared with the prototypical tunable plasmonic particles, gold nanoshells, as well as approximately 2-fold higher X-ray absorption than a clinical iodine contrast agent. After intratumoral or i.v. administration, we fuse PEG-NR biodistribution data derived via noninvasive X-ray computed tomography or ex vivo spectrometry, respectively, with four-dimensional computational heat transport modeling to predict photothermal heating during irradiation. In computationally driven pilot therapeutic studies, we show that a single i.v. injection of PEG-NRs enabled destruction of all irradiated human xenograft tumors in mice. These studies highlight the potential of integrating computational therapy design with nanotherapeutic development for ultraselective tumor ablation.
Figures





References
-
- Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA. Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science. 1997;277:1078–81. - PubMed
-
- Grubisha DS, Lipert RJ, Park HY, Driskell J, Porter MD. Femtomolar detection of prostate-specific antigen: an immunoassay based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering and immunogold labels. Anal Chem. 2003;75:5936–43. - PubMed
-
- Jackson JB, Westcott SL, Hirsch LR, West JL, Halas NJ. Controlling the surface enhanced Raman effect via the nanoshell geometry. Appl Phys Lett. 2003;82:257–9.
-
- Qian XM, Peng XH, Ansari DO, et al. In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surfaceenhanced Raman nanoparticle tags. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:83–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

